Figure 3.
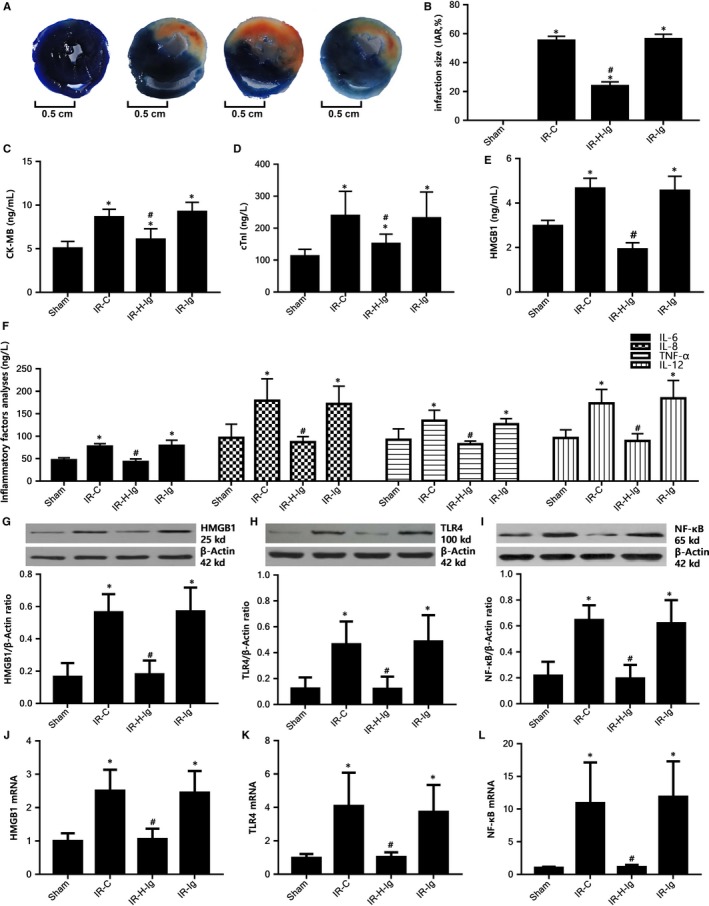
High‐mobility group protein box‐1 (HMGB1) antibody attenuates myocardial injury through mediating the role of dendritic cells (DCs) regulated by the HMGB1‐TLR4 signalling pathway. A, Comparison of myocardial infarct size among all groups (n = 6 for each group). Anti‐HMGB1 treatment reduces myocardial IR injury. Representative images of the infract area (INF: white), area at risk (AAR: red and white), and normal area (blue). B, Quantitative analysis of infarct size and the INF/AAR ratio (IAR, %). Comparison of concentrations of serum CK‐MB, cTnI, HMGB1, and IL‐6, IL‐8, TNF‐α, IL‐12 among all groups (n = 10 for each group). Blood was collected right after the IR procedure was completed. CK‐MB, cTnI, HMGB1, and IL‐6, IL‐8, TNF‐α, IL‐12 were measured as described in the Section 2. C, CK‐MB. D, CTnI. E, HMGB1. F, Inflammatory factors (IL‐6, IL‐8, TNF‐α, IL‐12). Comparison of protein and mRNA levels of HMGB1, TLR4, NF‐κB of cardiac tissues from rats of different groups (n = 10 for each group). Samples were collected right after IR procedure was completed. G, Western blot analysis of HMGB1 protein expression; H, Western blot analysis of TLR4 protein expression; I, Western blot analysis of NF‐κB protein expression; (J) relative expression of HMGB1 mRNA; (K) relative expression of TLR4 mRNA; (L) relative expression of NF‐κB mRNA. *P < 0.05, comparisons of IR‐C, IR‐H‐Ig and IR‐Ig groups with Sham group; #P < 0.05, comparisons of IR‐H‐Ig and IR‐Ig group with IR‐C group
