Figure 7.
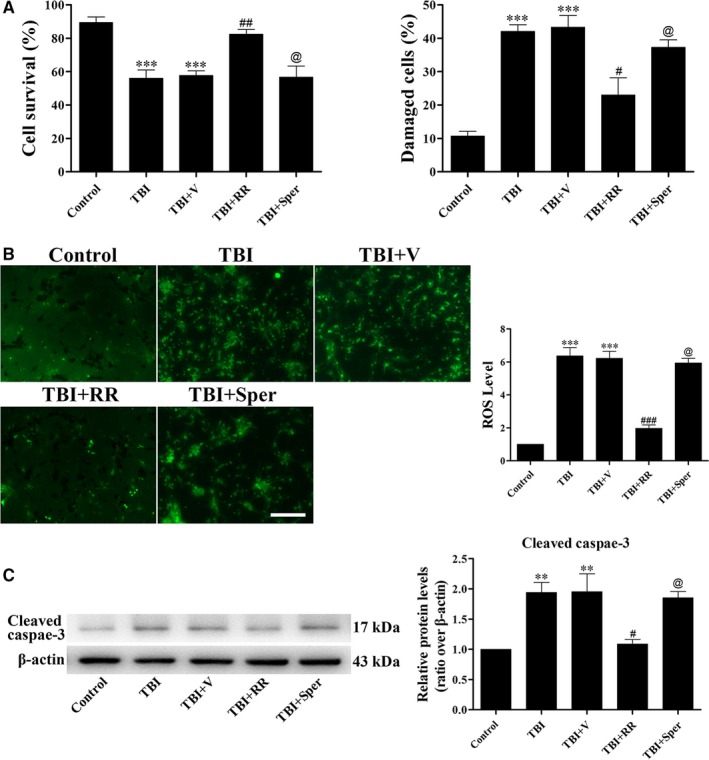
Ruthenium red (RR) instead of Sper treatment protected primary cultured neurons from traumatic brain injury (TBI). (A) Primary cortical neurons were subjected to scratch injury and then treated with RR (10 μM), Sper (10 μM) or saline for 1 day. The LDH release assay and TB staining were used to evaluate cell viability. The percentage of damaged cells significantly increased after TBI compared to the control group. RR treatment significantly decreased damaged cells after TBI, however, Sper treatment had no significant impact compared to the TBI + vehicle group. (B) Cells were subjected to scratch injury and subsequently treated with RR (10 μM), Sper (10 μM) or saline for 1 day. Then cells were incubated with DCFH‐DA and subjected to fluorescent microscopy analysis. The intracellular ROS was significantly increased after TBI compared to the sham group, and administration of RR instead of Sper significantly repressed ROS production as compared to the TBI + vehicle group. (C) RR (10 μM) treatment significantly decreased the expression of cleaved caspase‐3 after TBI, however, Sper treatment had no obvious effect. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 6 per group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs control group; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001 vs TBI + vehicle group; @ P > 0.05 vs TBI + vehicle group. β‐actin was used as a loading control. Scale bar: 50 μm
