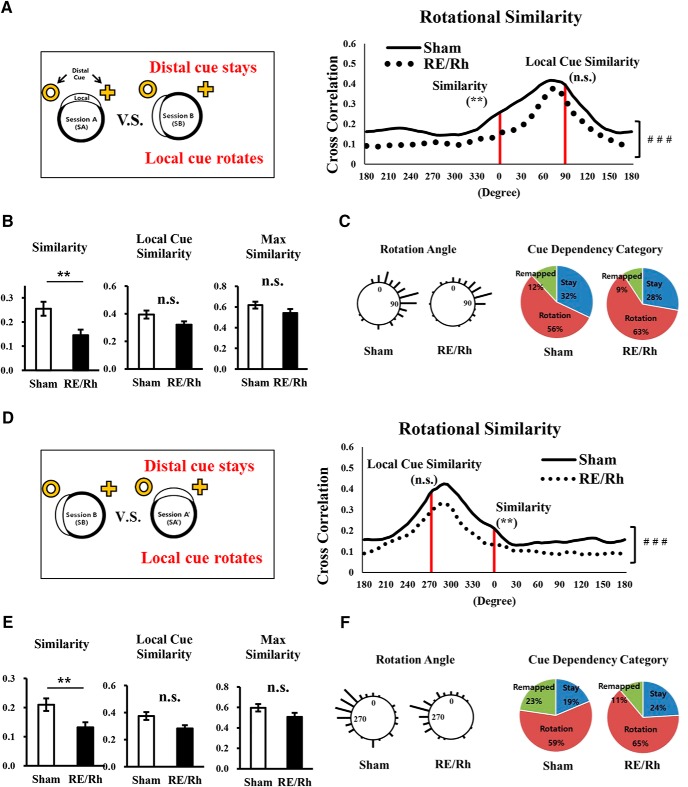
Figure 6.
Similarity analyses with cue rotation. A–C, Place cell representation analyses comparing SA and SB. A, Distributions of rotational similarity from the two groups were significantly different (overall group effects, ### p < 0.001). B, Similarity score was significantly decreased in the RE/Rh group. Local cue similarity and maximum similarity scores were not significantly different between groups (unpaired two-tailed t test, **p < 0.01). C, Distributions of rotation angles where maximum similarity was calculated and cue dependency categories of individual place cell responses. Stay contains neurons with rotation angle of 315∼45°; rotation contains neurons with rotation angle of 45∼135° following the local cue; remapping are the remaining cells that are not classified as stay or rotation). D–F, Place cell representation analyses comparing SB and SA′. D, Distributions of rotational similarity from the two groups were significantly different (overall group effects, ###p < 0.001). E, Similarity score was significantly decreased in the RE/Rh group. Local cue similarity and maximum similarity score were not significantly different between groups (unpaired two-tailed t test, **p < 0.01). F, Distributions of rotation angles and cue dependency categories of individual place cell responses. Stay contains neurons with the rotation angle of 315∼45°; rotation contains neurons with rotation angle of 225∼315° following the local cue; remapping contains cells that are classified as neither stay nor rotation.