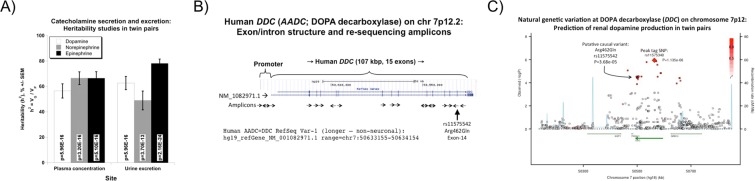
Figure 1.
Renal DA excretion: Effects of heredity and the DDC gene. (A) Heritability (h2) of catecholamine secretion and urinary excretion. Results for plasma catecholamine concentrations (pg/ml) and urine catecholamine excretion (ng/gm creatinine) emerge from variance components analyses by SOLAR in MZ versus DZ twin pairs. h2 is expressed as % of trait variance attributable to gene action, ±SEM. VG: genetic variance; VP: total phenotypic variance. (B) Human DOPA decarboxylase (DDC): Exon/intron and inter-species sequence conservation. Polymorphism discovery across the human DDC locus: re-sequencing strategy. There are 15 exons at human DDC. Eighteen polymerase chain reaction amplicons spanned the promoter and coding regions. Amplicons with double arrows were read in both directions. The SNP Arg462Gln (rs11575542) characterized in this paper is located in exon-14. (C) Natural genetic variation at DOPA decarboxylase (DDC, AADC) on chromosome 7p12: Prediction of renal DA production in twin pairs. Local region of the Manhattan plot displayed by SNAP (SNP Annotation and Proxy Search) plot http://www.broadinstitute.org/mpg/snap/ldplot.php. The peak association (p = 1.35E-06; see diamond) was at DDC intron-5 tagging SNP rs11575340. The DA secretion trait-associated coding variant (characterized in this paper) is at DDC Arg462Gln (exon-14, rs11575542). Marker-on-marker LD is shown as R2 (with respect to rs11575340), on a red color scale.