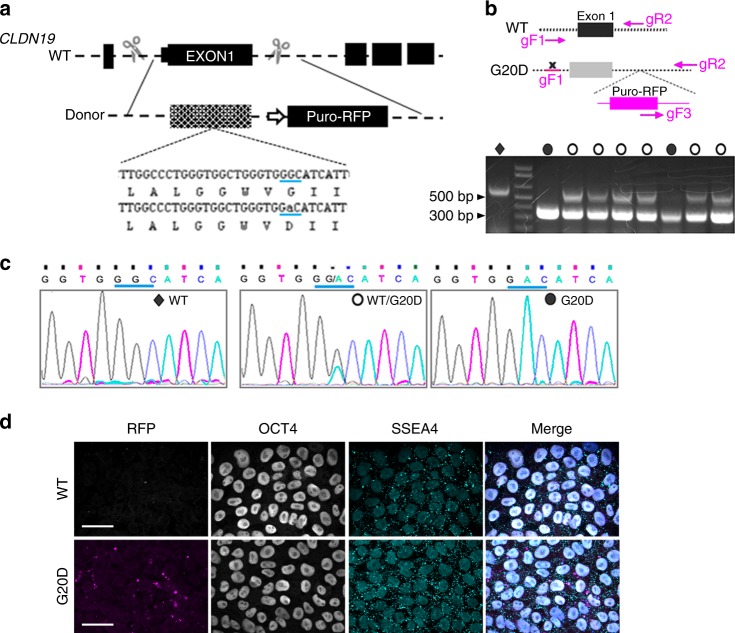
Fig. 1.
Strategy for creating mutants and expressing them in two-dimensional (2D) cultures. a Schema for introducing the G20D mutation into exon 1 using CRISPR/Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9) technology. The strategy includes adding a puromycin-red fluorescent protein (RFP) gene with a CAG promoter into the following intron. b The schema indicates the strategy for PCR-based genotyping of CLDN19 human induced pluripotent cell clones, and the gel shows the result. The uncropped gel is in Supplementary Figure 1. The gF1 primer binds within the promoter region; gR2 primer binds within intron 1; gF3 primer binds within the donor plasmid. For homozygous wild-type (WT) clones, the gF1/gR2 primer combination would yield a product of 550 base pairs. For homozygous clones with an insert, the gF3/gR2 primer combination would dominate to yield a 300-base pair product. Heterozygotes would yield both products. c DNA sequencing confirmed the genotype. d Confocal images of S34 (WT) and RFP-positive (G20D) clones demonstrated expression of the pluripotency markers SSEA4 (in the cytoplasm) and OCT4 (in the nucleus), as revealed by indirect immunofluorescence imaging. The merge images include 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) to indicate cell nuclei. Diamonds indicate wild type, open circles heterozygote and closed circles homozygote. Scale bar, 20 µm. Supporting data are included in Supplementary Information