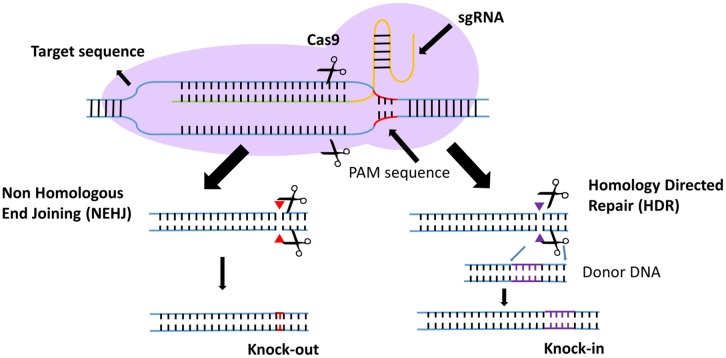
Figure 2.
Introduction to the CRISPR gene-editing system. Guided by sgRNAs, the CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease can target short DNA sequences. The PAM specifically creates a sgRNA–target DNA heteroduplex and generates double-strand breaks. Then, the DNA double-strand breaks are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). In the NHEJ pathway, indels lead to nucleotide deletions or insertions. In the HDR pathway, accessory factors can facilitate genome recombination through the two homology arms, resulting in the knock-in of a gene of interest.