Figure 3.
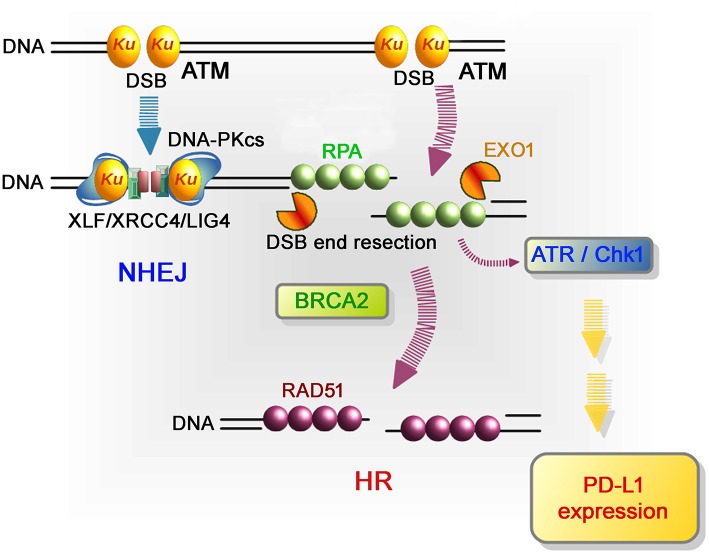
Repair pathways and signaling in response to DSB induction by IR. After DSB induction, the Ku70/80 heterodimer complex (Ku) rapidly binds to all DSB ends. Ku bound to DSB ends plays the following roles: 1) Ku70/80 complex promotes NHEJ and 2) Ku70/80 complex protects DNA ends from unscheduled digestion by DNA nucleases. In the NHEJ pathway, DSBs are rapidly rejoined by DNA-PKcs and XLF/XRCC4/LIG4 following Ku binding to DSB ends (81). On the other hand, DSB ends are digested in the 5′ to 3′ direction by EXO1 to direct repair pathway toward HR. The resected ssDNA is coated with RPA. BRCA2 promotes the protein switch from RPA to RAD51, facilitating strand invasion into the template strand for recombination-mediated repair. In terms of DNA damage signaling, ATM, which serves as a sensor of DSBs, is the major DNA damage response (DDR) kinase and is activated at unresected DSB ends. At DSB ends during HR, resection promotes a switch from ATM to ATR activation, followed by Chk1 activation. In the context of DNA damage-dependent PD-L1 expression, the activation of Chk1 is a critical step leading to STAT/IRF-mediated PD-L1 upregulation.