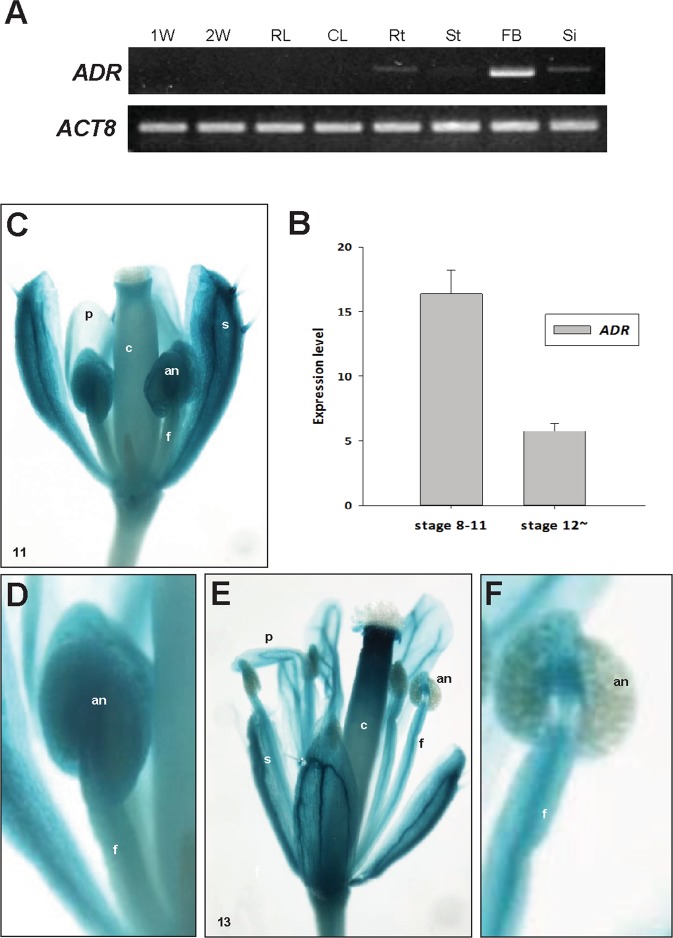
Figure 1.
Analysis of ADR expression in different Arabidopsis organs and GUS staining patterns in ADR::GUS Arabidopsis flowers. (A) The detection of ADR expression in different Arabidopsis organs. The mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR. Total RNA was isolated from 1-week-old seedlings (1W), 2-week-old seedlings (2W), rosette leaves (RL), cauline leaves (CL), roots (Rt), stems (St), floral buds (FB) and siliques (Si). The Arabidopsis ACTIN8 (ACT8) gene was used as internal controls. The grouping of two gels (ADR and ACT8) was cropped from two different original gels in Fig. S4. (B) The detection of ADR expression in wild-type flowers at two different developmental stages (8–11, >12). The mRNA levels were determined by real-time quantitative PCR. (C) In stage 11 of ADR::GUS young floral buds, GUS activity was strongly detected in the sepals (s) and anthers (an) of stamens but relatively weakly detected in the petals (p), carpels (c) and filaments (f) of stamens. (D) Close-up of the anther (an) from (C). (E) In stage 13 of ADR::GUS mature flowers, GUS was strongly detected in sepals (s), petals (p) and carpels (c). In the stamen, GUS activity was detected in the filaments (f) but was absent in the anthers (an) of stamens. (F) Close-up of the anther (an) from (E).