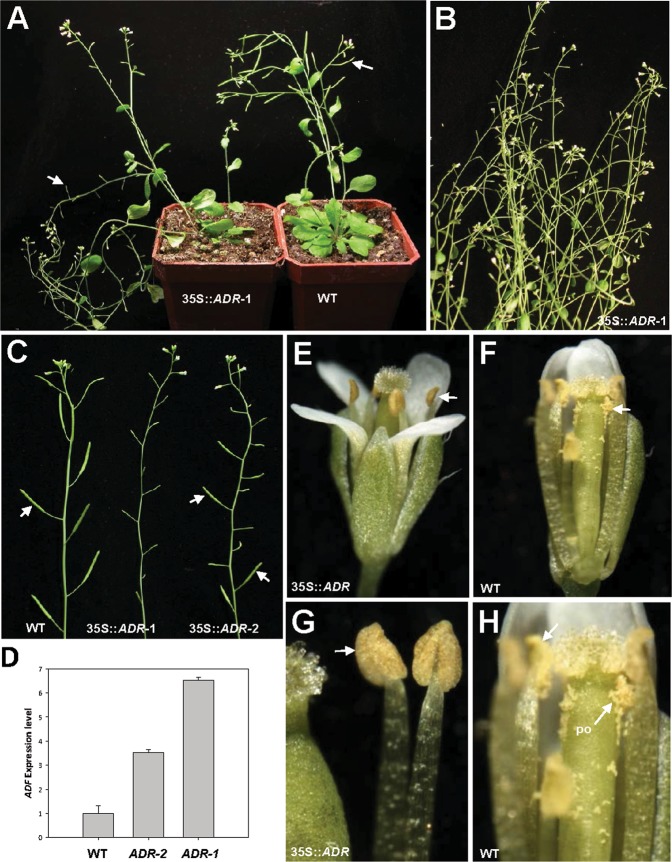
Figure 4.
Phenotypic analysis and the detection of gene expression in Arabidopsis plants ectopically expressing ADR. (A) A severe 44-day-old 35S::ADR plant (35S::ADR-1, left) was sterile and produced short siliques (arrowed), whereas wild-type plants (WT, right) produced long, well-developed siliques (arrowed). (B) Close-up of the inflorescences from a severe 35S::ADR (35S::ADR-1) plant during the late developmental stage. (C) Inflorescences from a severe 35S::ADR transgenic line (35S::ADR-1, middle) that showed sterility, a medium-severe 35S::ADR transgenic line (35S::ADR-2, right) that showed partial sterility and some partially elongated siliques (arrowed), and one wild-type plant (WT, left) with fully elongated siliques (arrowed). (D) Detection of gene expression in 35S::ADR transgenic Arabidopsis. mRNA accumulation for ADR was determined by real-time quantitative PCR. Total RNA isolated from flower buds before stage 12 of one wild-type plant (WT), one severe 35S::ADR-1 plant (ADR-1) and one medium-severe 35S::ADR-2 plant (ADR-2) was used as templates. The transcript levels of ADR were determined using three replicates and were normalized against that of UBQ10. Gene expression levels in 35S::ADR plants are presented relative to that of the wild-type plants, which was set at 1. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Each experiment was repeated twice and resulted in similar results. (E,F) Indehiscent anthers (arrowed) were observed in 35S::ADR plants (E) compared to wild-type plants, which showed normal anther dehiscence and pollen (arrowed) release (F). (G) Close-up of the 35S::ADR indehiscent anthers (arrowed) from (E). (H) Close-up of the wild-type dehiscent anthers (arrowed) with released pollen (po) from (F).