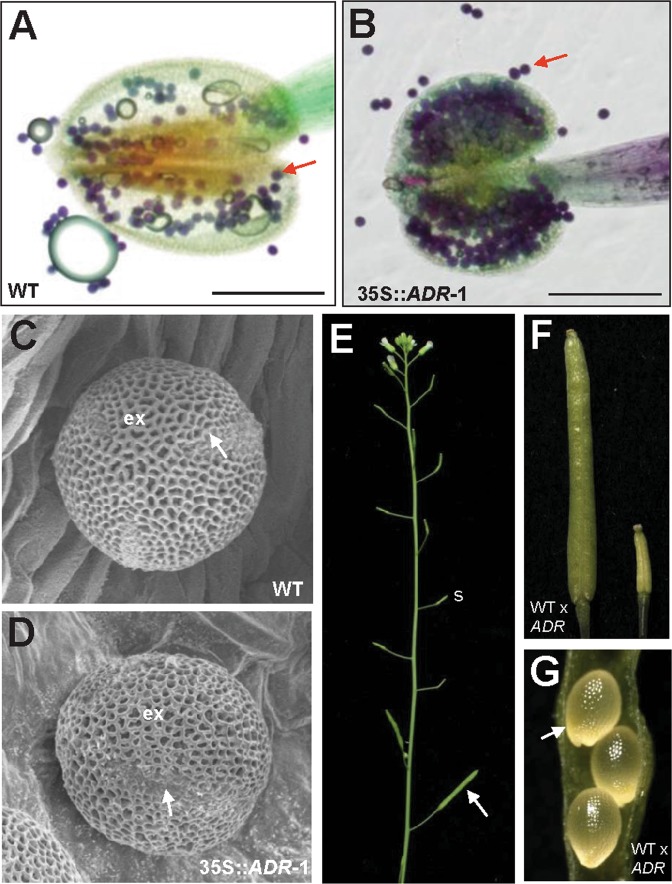
Figure 5.
Alexander’s staining and scanning electron microscopy of pollen produced in wild-type and 35S::ADR flowers and cross-pollination of wild-type pollen to 35S::ADR plants. (A,B) Pollen grains with normal viability (arrowed, stained dark purplish red) were observed in both the wild-type (A) and severe 35S::ADR anthers (B). (C,D) Close-up of the egg-shaped wild-type (C) and severe 35S::ADR (D) pollen grains. Colpi (arrowed) and outer exine (ex) with a typical irregular wall structure were observed on the surface of pollen. (E) The 35S::ADR flower that was manually pollinated with wild-type pollen developed well-elongated siliques (arrowed), whereas short siliques (s) developed without manual pollination. (F) Close-up of a well-elongated silique (WT x 35S::ADR) (left) and a short silique (right) from (E). (G) 35S::ADR ovules developed into normal embryos (arrowed) after manual pollination with wild-type (WT x 35S::ADR) pollen grains.