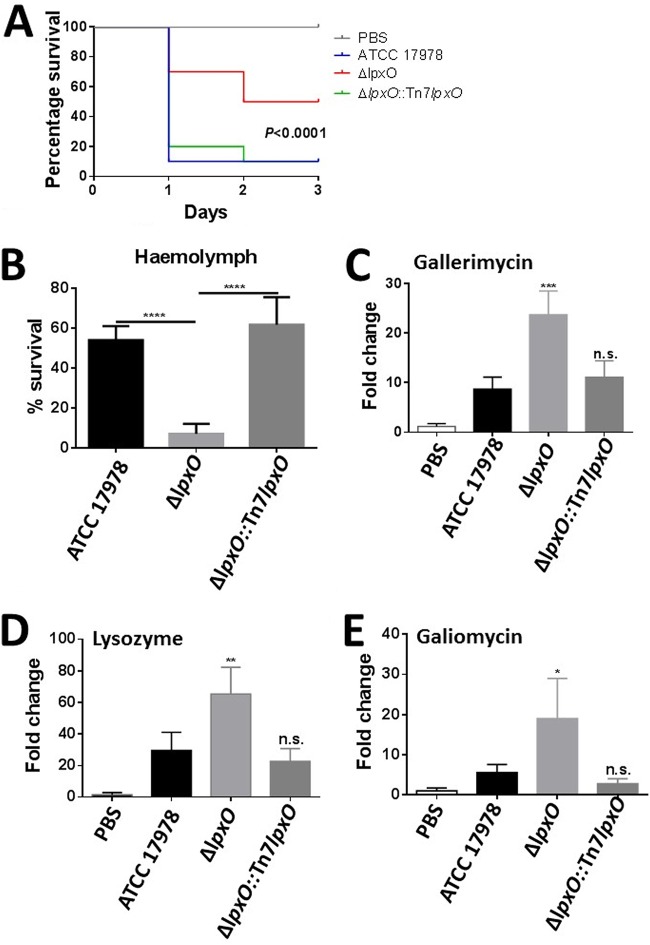
FIG 5.
A. baumannii lpxO mutant displays decreased virulence in the G. mellonella waxworm infection model. (A) Percent survival of G. mellonella over 72 h postinfection with 5 × 104 organisms of A. baumannii ATCC 17978, A. baumannii ΔlpxO mutant (ΔlpxO), and A. baumannii ΔlpxO::Tn7lpxO mutant (ΔlpxO::Tn7lpxO). Thirty larvae were infected in each group. Level of significance was determined using the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. (B) Percent survival of A. baumannii ATCC 17978, A. baumannii ΔlpxO mutant (ΔlpxO), and A. baumannii ΔlpxO::Tn7lpxO mutant (ΔlpxO::Tn7lpxO) following 1 h of exposure to G. mellonella hemolymph obtained from larvae challenged with heat-killed E. coli. (C to E) G. mellonella antimicrobial peptide expression determined after 12 h of infection with A. baumannii ATCC 17978, A. baumannii ΔlpxO mutant (ΔlpxO), and A. baumannii ΔlpxO::Tn7lpxO mutant (ΔlpxO::Tn7lpxO) by reverse transcriptase quantitative real‐time PCR. Three larvae per group were infected, and values are presented as the means ± SD from two independent cDNA preparations measured in duplicate. In panels B to E, P values were <0.05 (*), 0.01 (**), <0.001 (***), and <0.0001 (****) versus A. baumannii ATCC 17978, determined using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni contrasts.