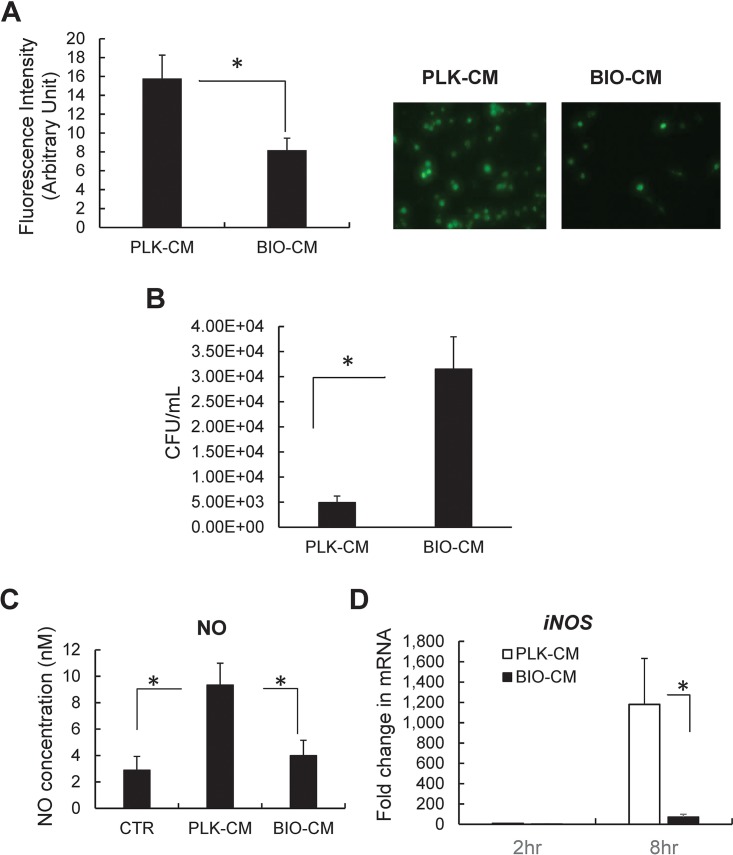
FIG 1.
Effects of S. aureus biofilm-conditioned medium on the phagocytic and bactericidal capacities of RAW 264.7 macrophages. (A) Effect of S. aureus biofilm on the phagocytic activity of macrophages. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with conditioned medium from either a planktonic culture (PLK-CM) or a biofilm culture (BIO-CM) of S. aureus for 2 h. Next, the extent of bacterial phagocytosis by RAW 264.7 cells was assessed by measuring the fluorescence intensity from the phagocytized bacteria (opsonized Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated E. coli). (Left) Quantification of phagocytosis (n = 8). (Right) Representative fluorescence images of RAW 264.7 cells. (B) Effect of S. aureus biofilm on the bactericidal activity of macrophages. RAW 264.7 cells were exposed to PLK-CM or BIO-CM for 2 h and then incubated with live S. aureus bacteria for 1 h, followed by an antibiotic protection assay to count the number of intracellular S. aureus bacteria that survived within macrophages (n = 5 per group). (C) Effect of S. aureus biofilm on secretion of nitric oxide from RAW 264.7 macrophages. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with normal culture medium (control [CTR]), PLK-CM, or BIO-CM for 8 h, and nitric oxide concentrations in the supernatant of the cell culture were measured. (D) qPCR analysis of iNOS mRNA from RAW 264.7 cells 2 and 8 h following treatment with PLK-CM or BIO-CM (n = 8). *, P < 0.05.