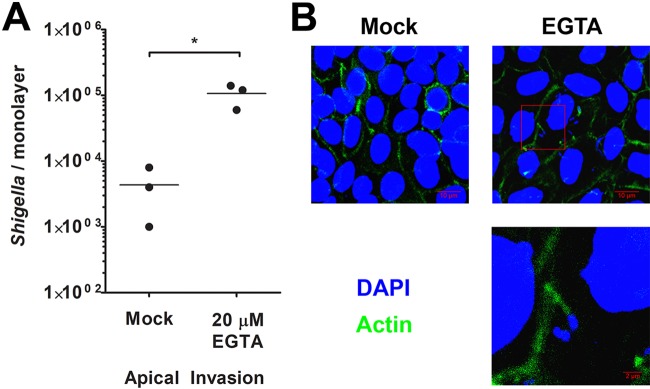
FIG 6.
Disrupting colon enteroid tight junctions enables Shigella apical access to the host cytosol. (A) Colon enteroid monolayers were treated with EGTA, and S. flexneri bacteria were then introduced apically and enumerated at 3 h p.i. Mock indicates monolayers not treated with EGTA (PBS only). * indicates statistical significance, determined by a t test (n = 3; P < 0.05). (B) Confocal microscopy was used to visualize colon enteroid monolayers treated with EGTA and apically invaded by S. flexneri. Monolayers were stained with DAPI (blue) and phalloidin (green). Micrographs are average-intensity projections of a z-stack. An enlarged portion of the micrograph from EGTA-treated colonoids, annotated by a red box, highlights a Shigella cell associated with an actin tail.