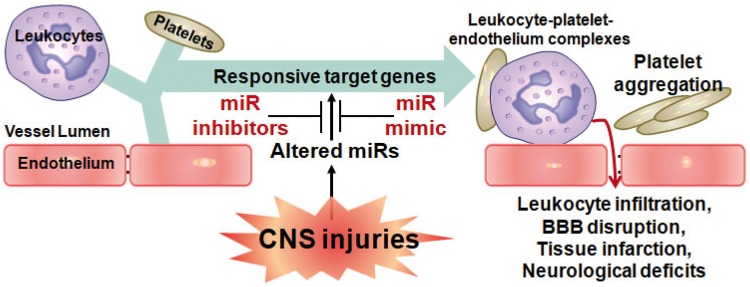
Figure 2.
Function of circulating microRNAs in CNS injuries. During CNS injuries, decreased miRNAs in blood lead to upregulation of their target inflammatory genes and blood clotting genes, and thus results in multiple outcomes after CNS injuries, including leukocyte-platelet-endothelium complexes, platelet aggregation, leukocyte infiltration, BBB disruption, tissue infarction, neurological deficits, and others. MiRNA mimics replace the decreased miRNAs in blood and accordingly attenuate these detrimental outcomes after CNS injuries.