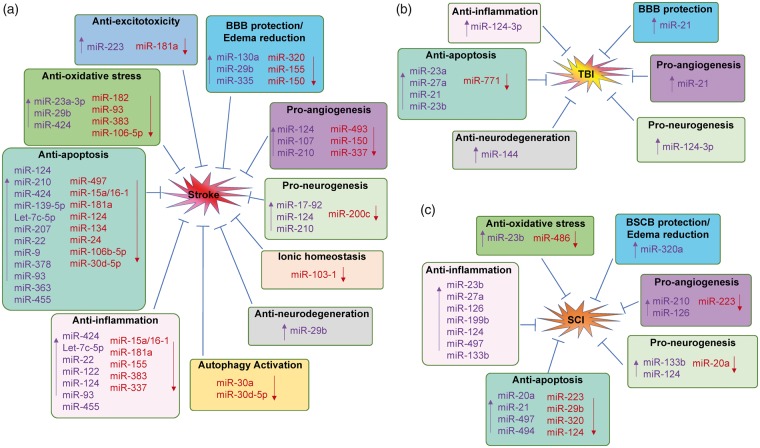
Figure 5.
Mechanisms of microRNA-based therapeutics for CNS injuries. Therapeutic mechanisms of microRNA-based drugs for stroke (A), traumatic brain injury (TBI, B) and spinal cord injury (SCI, C). (a) Upregulation or downregulation specific miRNAs in the brain exhibits protective effects against stroke via different mechanisms, including anti-excitotoxicity, anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, BBB protection and edema reduction, pro-angiogenesis, pro-neurogenesis, anti-neurodegeneration, maintain ionic homeostasis and activation of autophagy. (b) Manipulation of several miRNAs exerts neuroprotection again TBI through mechanisms involving anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, BBB protection, pro-angiogenesis, pro-neurogenesis and anti-neurodegeneration. (c) A number of miRNAs are also involved for the potential therapy of SCI through various mechanisms, including anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, anti-neurodegeneration, BSCB protection and edema reduction, pro-angiogenesis and pro-neurogenesis. Moreover, many miRNAs possess the ability to regulate the pathophysiological events against CNS injuries via several different mechanisms. “↑”, upregulate miRNA levels by miRNA mimics; “↓”, downregulate miRNA levels by miRNA inhibitors.