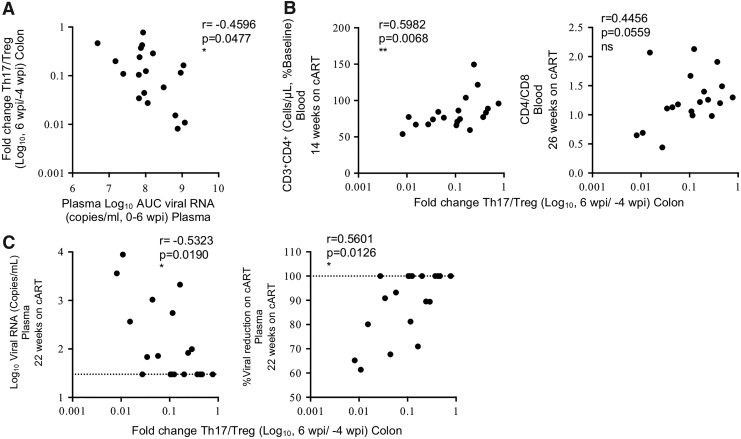
FIG. 4.
Maintenance of the gut Th17/Treg ratio correlates with improved virological response to cART. (A) Correlation between acute SIV plasma viral load (viral RNA copies/mL), measured as AUC 1–6 wpi, versus log10-fold change in the Th17/Treg ratio during acute infection compared to preinfection levels (log10 6 wpi/−4 wpi). (B) Correlations between log10-fold change in Th17/Treg ratio during acute infection (6 wpi/−4 wpi) versus restoration of peripheral blood CD4 counts as percent of preinfection levels during cART (left panel) or CD4/CD8 ratio (right panel) (14–26 wpi). (C) Correlations between log10-fold change in Th17/Treg ratio during acute infection (6 wpi/−4 wpi) versus plasma viral RNA (left panel) or percent viral reduction in the plasma (right panel) after 22 weeks on cART. Percent viral reduction on cART using the limit of viral detection for the assay of 30 copies/mL of plasma was calculated as follows: [(log FVL/IVL)/(log 30/IVL)]*100, where FLV = final viral load measured after 22 weeks on cART, IVL = initial viral load measured at 6 wpi when cART was first initiated. The dotted line indicates the limit of detection of the assay (left panel) or maximum percentage (100%) of viral reduction (right panel). Spearman's rank correlation coefficients are shown, with p-values ≤0.05 considered significant. AUC, area under the curve.