Figure 2.
Compartmentalization of the ciliary membrane.
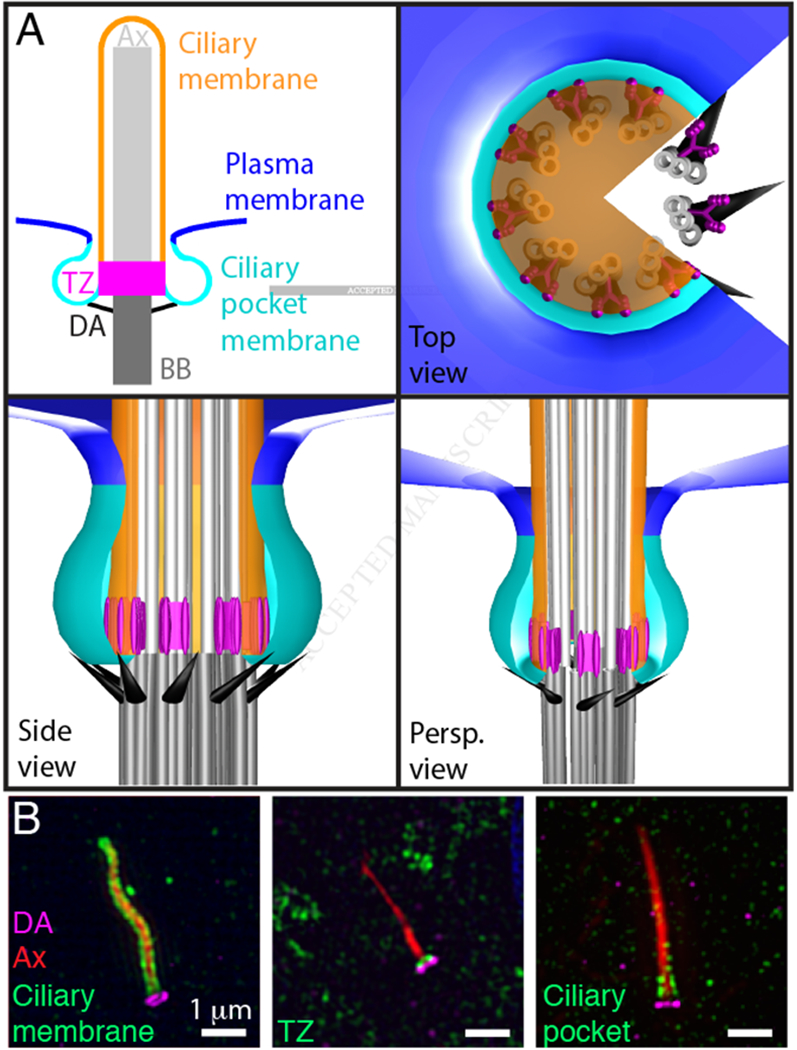
(A) The basal body (BB, dark grey) consists of nine-fold triplet microtubules. Doublet microtubules extend from the basal body to form the ciliary axoneme (Ax, light grey). Distal appendages (DA, black) project from the triplet microtubules at the distal end of the basal body. The transition zone (TZ, magenta) is a subdomain of the base of the cilium characterized by Y-shaped links between the ciliary membrane and doublet microtubules of the axoneme. The ciliary membrane (orange) ensheaths the axoneme. The ciliary pocket membrane (cyan) surrounds the ciliary membrane and separates it from the plasma membrane (blue). The plasma membrane, ciliary pocket, and the ciliary membrane are continuous. Panels depict a twodimensional model of the cilium (top left) or top, side, and perspective views (Persp.) of a three dimensional model.
(B) SIM detection of the distal appendages (CEP164, magenta), the axoneme (acetylated Tubulin, red) and either the ciliary membrane (ARL13B, green), the transition zone (TCTN2, green), or the ciliary pocket (EHD, green). Immunofluorescence staining and SIM were performed according to protocols described in [52].
