Figure 6:
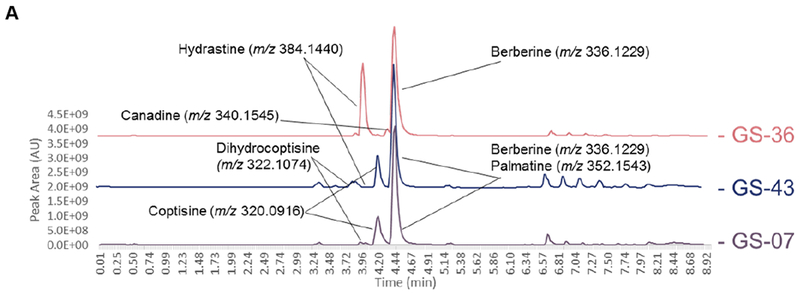
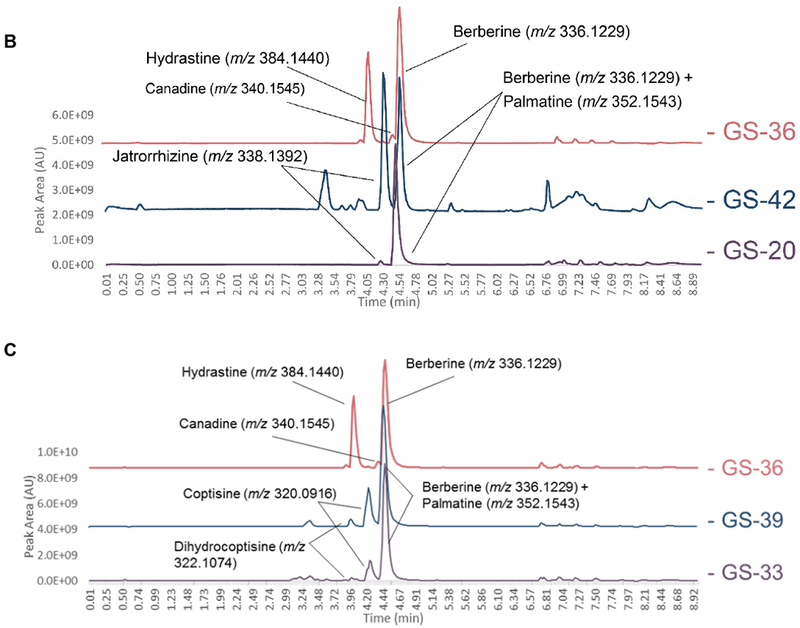
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) chromatograms from supplement samples GS-07 (A), GS-33 (B), and GS-20 (C) (suspected to be altered compared against reference material profiles for H. canadensis (GS-36), C. chinensis (GS-39), B. vulgaris (GS-43), and M. Aquifolium (GS-42). Highlighted alkaloid peaks are identified through comparison of accurate mass from high-resolution mass spectrometry in the positive ionization mode. GS-07 and GS-33 revealed peaks corresponding to berberine, palmatine, coptisine, and dihydrocoptisine, the last three of which are not found in the H. canadensis reference material. The M. aquifolium standard possessed berberine, palmatine, and jatrorrhizine; all of which were also present in GS-20 but the latter two were found in much lower concentrations than what was observed in the M. aquifolium reference material.
