Figure 2: Nucleic acid sensing and the host-virus conflict.
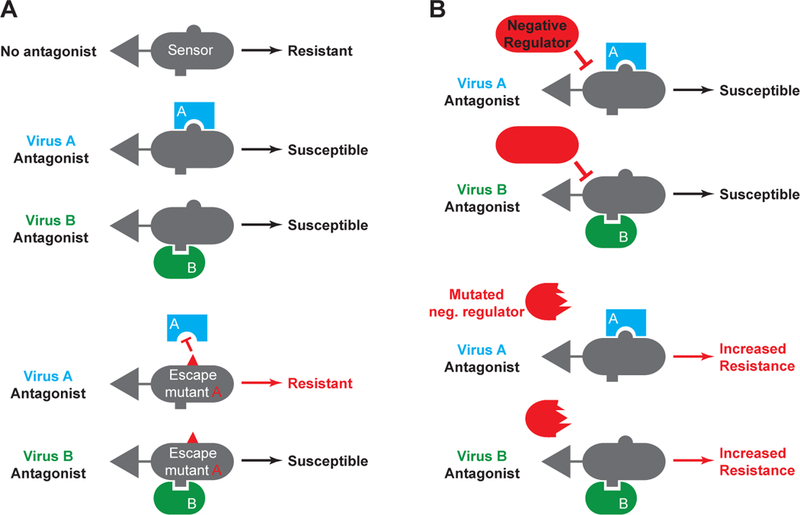
A: Two viruses are shown, each of which encodes a distinct antagonist of the same sensing pathway. An escape mutation in the sensor that overcomes antagonism by virus A does not impact continued antagonism by virus B. B: A mutation in a pathway-specific negative regulator increases the overall strength of the sensing pathway, conferring increased resistance to both viruses even in the presence of their antagonists.
