Figure 2.
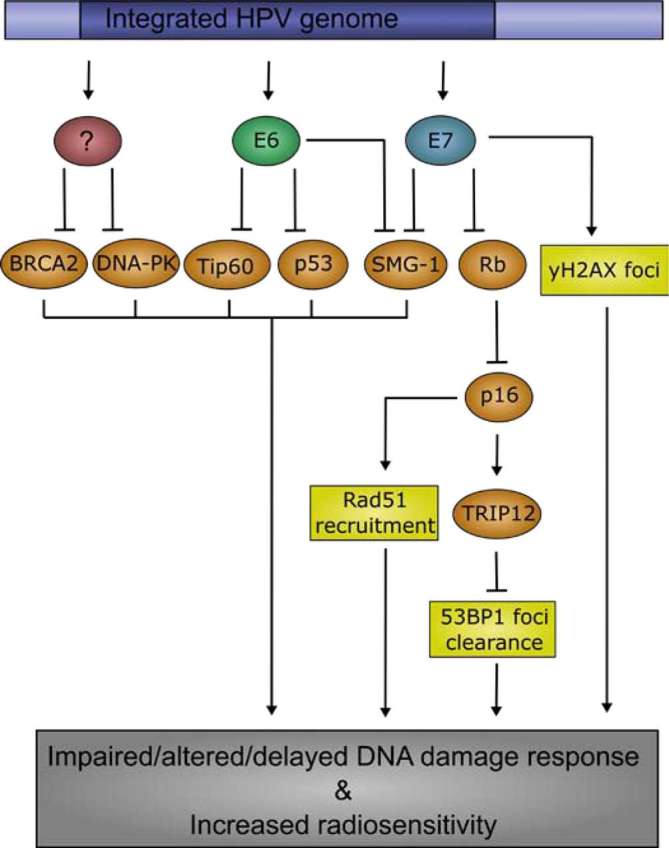
Mechanisms contributing to an altered DDR and increased radiosensitivity in HPV-positive HNSCC Infection with HPV, and subsequent expression of E6 and E7, contribute to an altered DDR in HNSCC tumour cells. E6, E7, and possibly other un-described mechanisms, repress DNA damage signalling transducers and effectors, such as SMG-1, p53, and BRCA2. Irradiation of HPV-positive tumour cells causes significantly more yH2AX and RAD51 foci than in HPV-negative tumour cells. Additionally, it is believed that HPV-positive tumour cells have a delay in DSB repair, as measured by 53BP1 foci clearance, indicating that HPV-positive tumour cells have impaired DSB repair mechanisms, contributing to their intrinsic radiosensitivity. DDR, DNA damage response; DSB, double strand breaks; HNSCC, head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma; HPV, human papilloma virus.
