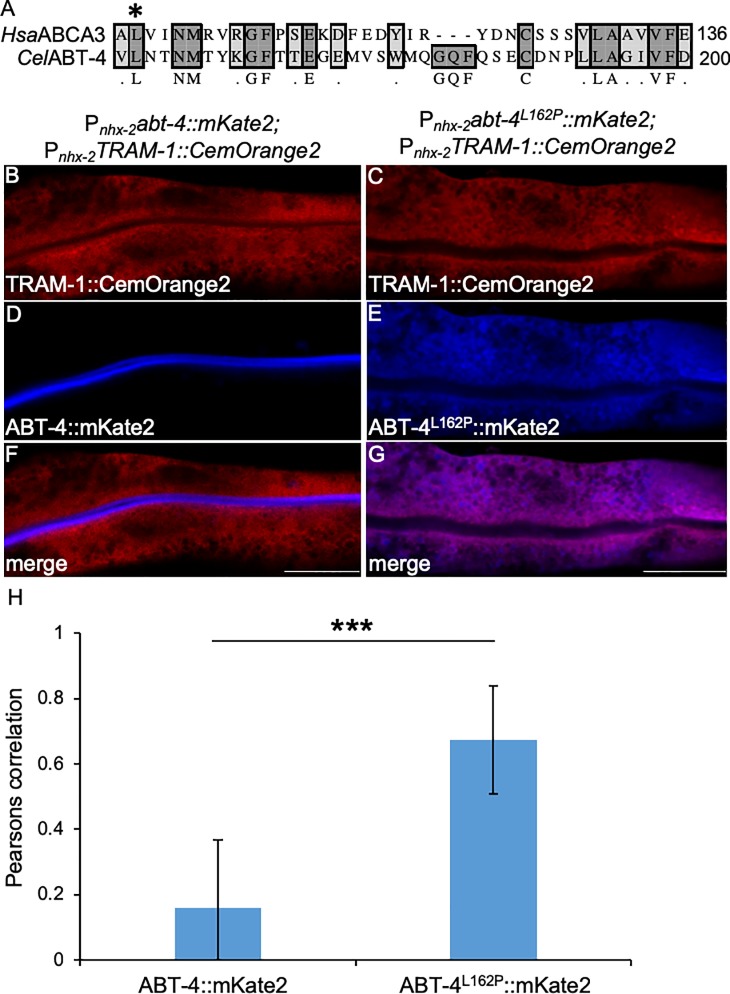
Fig 7. A CemOrange2 marker co-localizes a mutant ABC transporter protein to the ER.
Alignment of the primary amino sequence from human (Hsa) ABCA3 (Accession: AAH20724.1) and C. elegans (Cel) ABT-4 (Accession: NP_503175.1) using the ClustalW algorithm (A). Only residues 100–136 of HsaABCA3 aligned with residues 161–200 from CelABT-4 are shown. The asterisk marks L101 (human numbering) or L162 (C. elegans numbering) in the alignment that is conserved between species. Pnhx-2abt-4::mKate2;Pnhx-2TRAM-1::CemOrange2 (B, D, F) or Pnhx-2abt-4L162P::mKate2;Pnhx-2TRAM-1::CemOrange2 (C, E, G) transgenic C. elegans strains were imaged by confocal microscopy using a 40x PlanApo oil immersion objective (N.A. 1.3) over >20 z-planes. Representative single XY regions are shown. ABT-4::mKate2 (D, pseudocolored blue) or ABT-4L162P::mKate2 (E, pseudocolored blue; Ex 594 nm/Em605-645 nm) and TRAM-1::CemOrange2 (B,C, orange; Ex549 nm/ Em560-580 nm), showed that ABT-4::mKate2 trafficked normally to the apical membrane in intestinal cells (F), whereas the single point mutation in ABT-4L162P triggered retention within the ER (G). Scale bar = 25 μm. (H) Colocalization between ABT-4 or ABT-4L162P and TRAM-1 (F and G, respectively) was determined using the Pearson correlation in Volocity image analysis software (v6.3) (***p<0.001; n≥10).