Figure 2. Msn2/4-Regulated Genes Are Strongly Induced by Heat Shock, yet Fail to Engage in Intergenic Interactions.
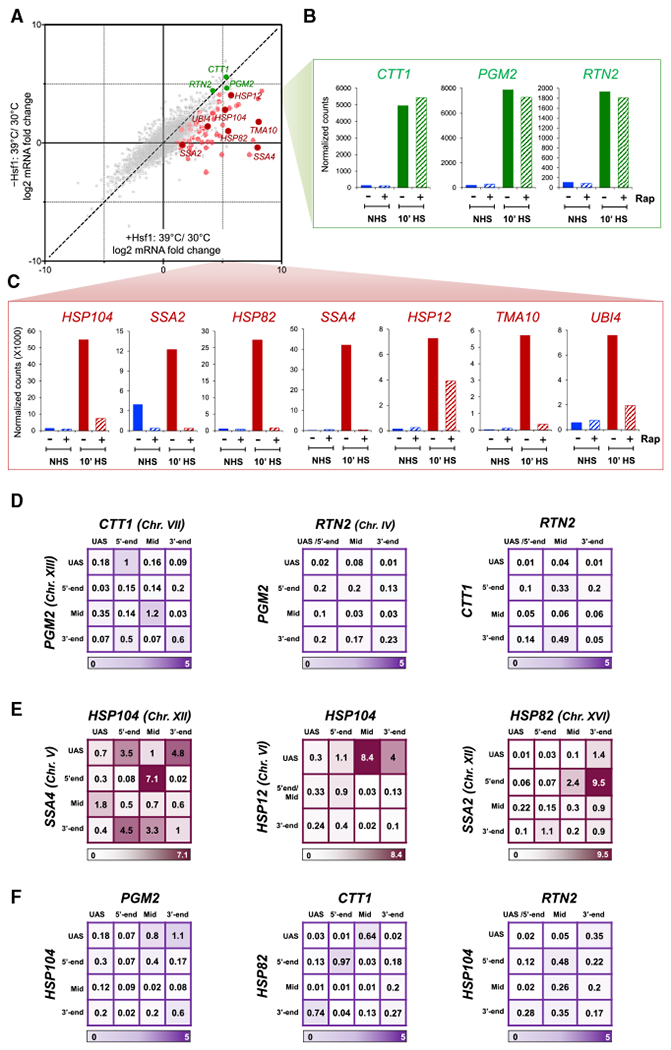
(A) Transcriptome-wide HS/NHS fold change in expression in the presence and absence of nuclear Hsf1 using the Hsf1 anchor away system (Hsf1-AA). Plotted are RNA-seq count ratios determined for every gene. Categories: red and pink, Hsf1-occupied genes in acutely heat-shocked cells (Pincus et al., 2018); green, Msn2/4-dependent, Hsf1-independent genes (as defined in text); gray, all others.
(B) Transcript levels (normalized RNA-seq reads) of select Msn2/4-dependent genes under each of the indicated conditions. Rap, rapamycin.
(C) As in B, except for select Hsf1-dependent genes.
(D) Matrix summaries of intergenic interaction frequencies between the indicated Msn2/4-target genes in 10 min HS cells (analysis and presentation as in Figure 1B). For each pairwise test, n = 2 and qPCR = 4.
(E) As in (D), except that pairwise tests were conducted between the indicated Hsf1-target genes.
(F) As in (D), except that intergenic interactions between Msn2/4- and Hsf1-regulated genes were determined.
See also Figures S1, S3, and S4.
