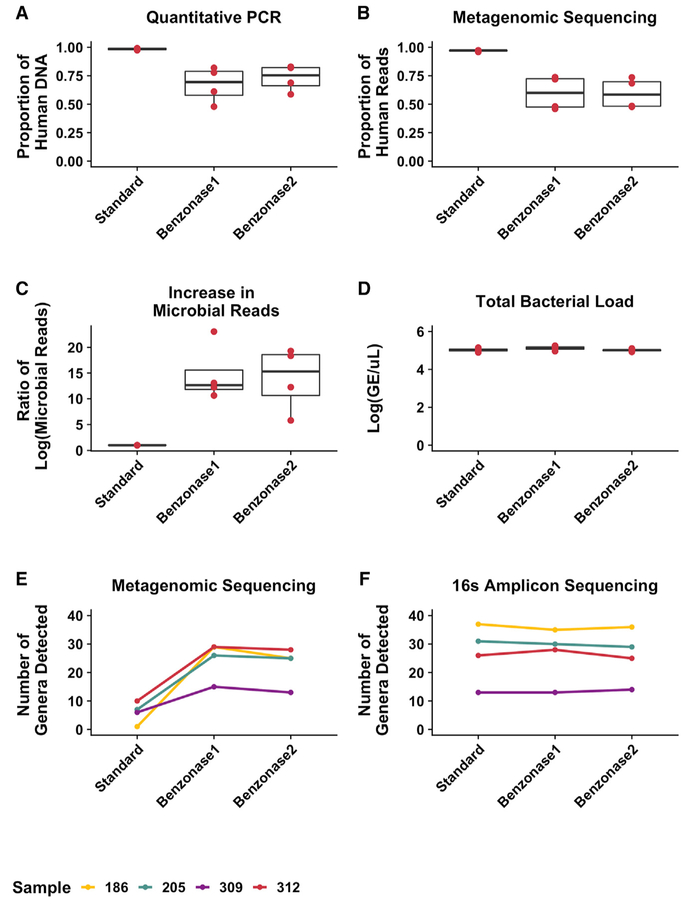
Figure 4. Effect of the Refined Benzonase2 Extraction Method on Selective Human DNA Depletion and Microbial Sequencing Depth.
Total DNA from the 4 test set 2 sputum samples was extracted using standard, benzonase1, and benzonase2 extraction methods and analyzed to show the following.
(A) Proportion of human DNA relative to total DNA as determined by qPCR.
(B) Proportion of human to total reads calculated by mapping all of the metagenomic sequencing reads to a reference human genome.
(C) Ratio of microbial shotgun sequencing reads yielded by each extraction method compared to the standard extraction.
(D) Total bacterial load (genome equivalents [GEs]) yielded from each extraction method, as determined by qPCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene. Boxes represent the interquartile region, and black lines indicate the median value.
(E and F) Number of genera detected in each extract using (E) metagenomic sequencing or (F) 16S amplicon sequencing. Each color represents a different sample.
Results from each extraction method were compared to the standard extraction conditions using pairwise, 2-sided t tests with a Benjamini-Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons, identifying no significant differences.