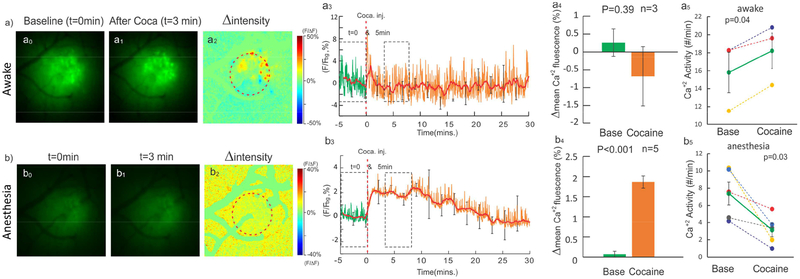
Figure 5.
Cocaine-induced neuronal [Ca2+]i changes in the awake and anesthetized states. a0a3) and b0-b3) Ca2+ fluorescence images before and after cocaine and their ratio images in the awake and anesthetized states. a3-b3) Time-lapse Δ[Ca2+]i (%) in the awake and anesthetized states. a4-b4) [Ca2+]i differences before (t=0min) and after (t=5min) were insignificant in the awake state [F(14,28)=1.1, p=0.39], but increased 1.86±0.15% [F(14,56)=8.16, p<0.001, n=5] in the anesthetized state. a5-b5) Ca2+ activities averaged over 5min before and after cocaine, which increased from 15.8±5.3count/min after cocaine: 18.2±3.2count/min (p=0.04) in the awake state but decreased from 7.4±2.9count/min to 3.16±1.7count/min (p=0.03) in the anesthetized state.