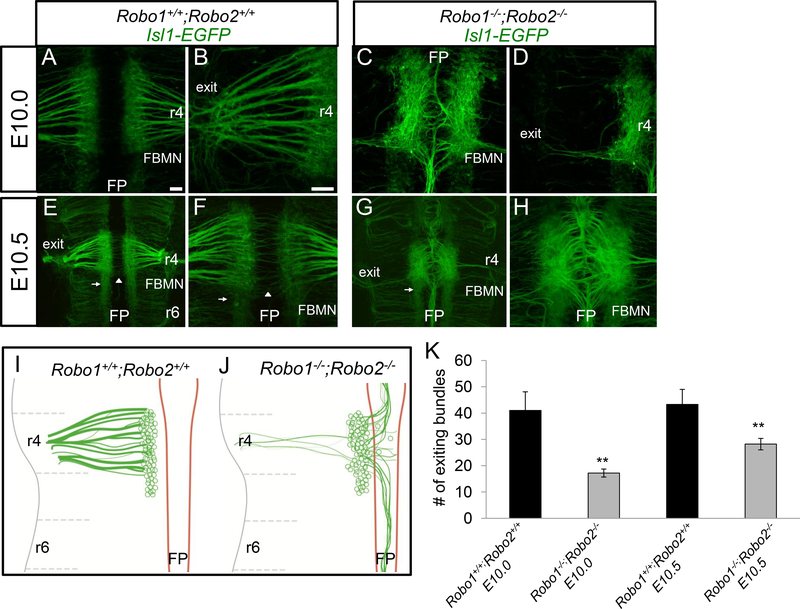
Figure 3. Robo1 and Robo2 are required to guide pioneer facial axons toward their r4 dorsal exit point.
E10.0-E10.5 open-book Isl1-EGFP hindbrains comparing control (A, B, E, F) and Robo1−/−;Robo2−/− (C, D, G, H) embryos. A-D. E10.0 mouse hindbrains arranged rostral, top; floor plate (FP), center. A, B. In control embryos, facial axons coursed from the facial branchiomotor nucleus (FBMN) towards the dorsal motor exit point (denoted as exit) in r4; a higher magnification view is shown in panel B. C. In Robo1−/−;Robo2−/− embryos, motor axons were misguided into the floor plate. Likewise, the nucleus was shifted closer to the floor plate. D. A higher magnification view in Robo1−/−;Robo2−/− mice to show that few axons projected dorsally from the FBMN to their exit point. E-H. By E10.5, facial axons did not self-correct after initial projection errors. E,F. On E10.5 in control, FBMN cell bodies migrated caudally (arrow). The commissural axons of the inner ear efferents (IEE) nerve (arrowhead) also crossed the midline. G. On E10.5, most facial axons did not project towards the exit point and instead projected in bundles rostrally and caudally in the floor plate. A reduced stream of neurons migrated caudally (arrow). H. High magnification of ventral midline. I, J. Schematics of E10.010.5 FBMN nerve projections, showing decreased axon projections toward the exit point, and a shift of projections into and longitudinally within the floor plate. The tangential caudal migration of cell bodies started on E10.5, and was characterized by a subpopulation of FBMN pioneering this route. K. Graph quantifying the number of facial axon bundles projecting to the r4 exit point in E10.0 and E10.5 control (black) compared to Robo1−/−;Robo2−/− mutants (gray). Scale 50 μm. Error bars show S.E.M.; significance was measured using students t-test, **p<0.01. n=4, E10.0 Robo1+/+;Robo2+/+. n=5, E10.0 Robo1−/−;Robo2-/−. n=3, E10.5 Robo1+/+;Robo2+/+ E10.5. n=5, Robo1−/−;Robo2-/−.