Figure 2. Effect of virion maturation on mAb neutralization.
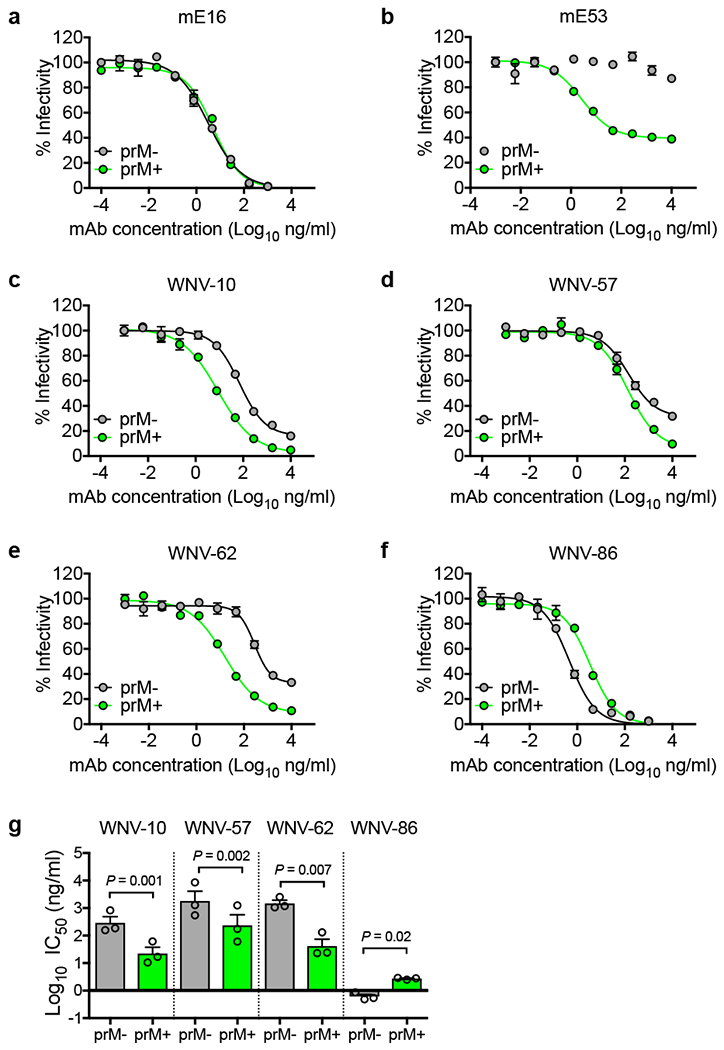
WNV RVPs prepared in the presence of overexpressed furin (prM-) or ammonium chloride (prM+) to increase or decrease the efficiency of virion maturation, respectively, were tested for sensitivity to neutralization by murine mAbs (a) mE16 and (b) mE53, or human mAbs (c) WNV-10, (d) WNV-57, (e) WNV-62, and (f) WNV-86. Shown are dose-response curves with infectivity normalized to levels observed in the absence of antibody representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Data points and error bars indicate the mean and range of duplicate infections, respectively. Mean IC50 values for each mAb (g) were obtained from three experiments. Error bars indicate SEM. The indicated P values were obtained from two-tailed paired t-tests. The mean difference between groups in panels g (and the 95% confidence interval of this difference) were as follows: WNV-10 [Log10 −1.11 (−1.29 to −0.94)]; WNV-57 [Log10 −0.89 (−1.05 to −0.73)]; WNV-62 [Log10 −1.5 (−2.11 to −0.99)]; WNV-86 [Log10 0.65 (0.23 to 1.06)].
