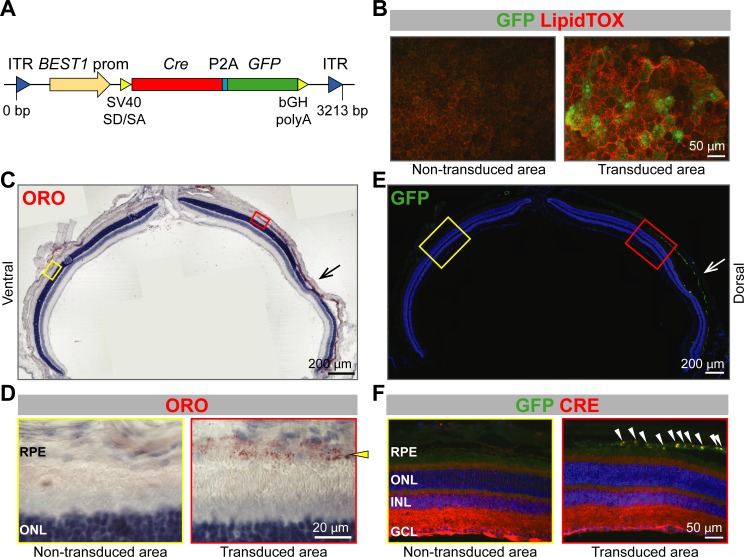
Figure 4. Lipid accumulation after AAV-mediated excision of Abca1 and Abcg1 in adult RPE.
(A) Schematic representation of the vector packaged into AAV4 capsid in order to express Cre and GFP specifically in the RPE of Abca1flox/flox;Abcg1flox/flox mice. Length of the construct in base pairs is shown below the map. ITR: inverted terminal repeat; SV40 SD/SA: simian virus 40 splice donor/splice acceptor site; P2A: porcine teschovirus 2A; bGH polyA: bovine growth hormone polyadenylation tail. 10 weeks after sub-retinal injections, co-localization of AAV-mediated Cre/GFP expression and lipid accumulation was analyzed by IF in RPE flat mounts (B) and retinal sections (C–F). (B) RPE flat mounts were stained with LipidTOX (red); shown are representative images of a non-transduced and a transduced area. Dorsal-ventral retinal sections were stained with ORO: retina panorama is shown in (C) and magnified images of a non-transduced and a transduced area (corresponding to yellow and red rectangles in the panorama) are shown in (D). Yellow arrowhead indicates LDs in the transduced RPE. Nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Consecutive retinal sections were analyzed for AAV transduction by IF: retinal panorama is shown in (E) and magnified pictures of a non-transduced and a transduced area (corresponding to yellow and red rectangles in the panorama) are shown in (F), together with CRE staining. White arrowheads indicate CRE-positive nuclei in the transduced RPE. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Black (C) and white (E) arrows indicate the injection site. Representative pictures of N ≥ 3 animals per group. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.