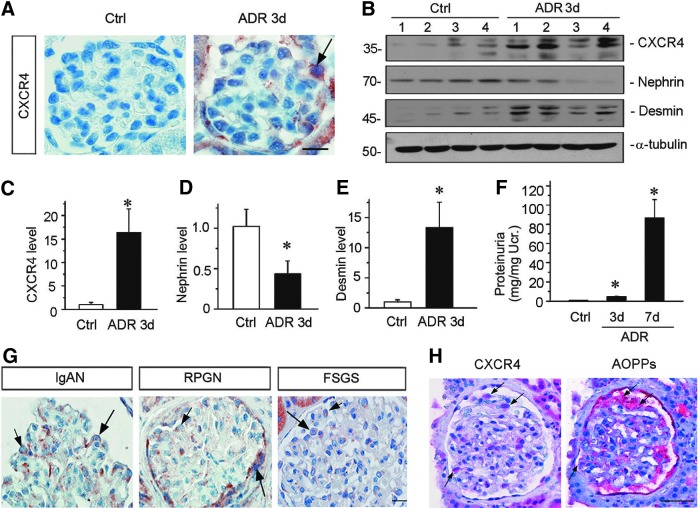
FIG. 1.
De novo expression of CXCR4 is induced in podocytes after kidney injury. (A) Immunohistochemical staining demonstrates CXCR4 expression in glomerular podocytes after ADR injury. Three days after ADR (10.5 mg/kg) injection, mice were sacrificed, and paraffin-embedded kidney sections were stained with CXCR4 antibody. Arrow indicates positive staining. Scale bar, 15 μm. (B) Western blotting analyses of renal expressions of CXCR4, nephrin, and desmin in control and ADR-injected mice. Numbers (1–4) represent different animals in a given group. (C–E) Graph presentations show the relative abundance of CXCR4 (C), nephrin (D), and desmin (E) protein expression in control (Ctrl) and ADR-treated (ADR 3d) groups. *p < 0.05 versus normal controls (n = 5–6). (F) Urinary albumin levels in mice at 3 and 7 days after ADR injection. Data are presented as mg/mg of urinary creatinine. *p < 0.05 versus normal controls (n = 5–6). (G) Representative images of CXCR4 staining in human IgAN, RPGN, and FSGS. Arrows indicate positive staining in podocytes. Scale bar, 15 μm. (H) Colocalization of CXCR4 and AOPPs in the glomeruli of the kidney biopsy from patient with IgAN. Kidney sequential paraffin sections were immunostained for CXCR4 and AOPPs. Colocalizations of CXCR4 and AOPPs in glomerular podocytes are indicated by arrows. Scale bar, 40 μm. All full unedited gels for Figure 1 are presented in Supplementary Figure S6. ADR, adriamycin nephropathy; AOPPs, advanced oxidation protein products; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; FSGS, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; IgAN, immunoglobulin A nephropathy; RPGN, rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.