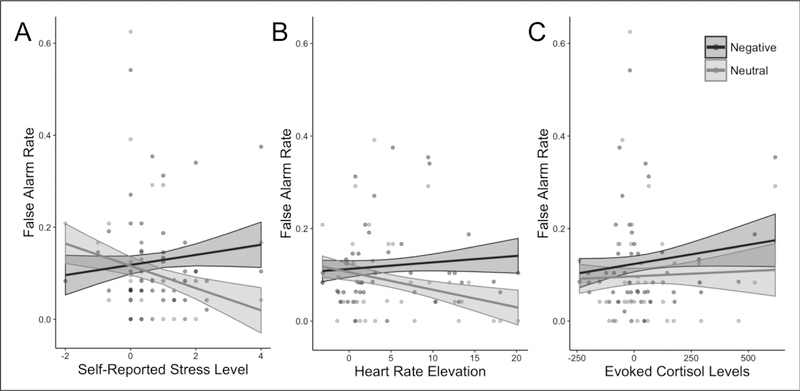
Figure 4.
Individual differences in stress and false alarms. Irrespective of group assignment, increases in evoked stress as assessed by A) self-report (N=47; F(1, 45) = 14.901; p = .001) and B) heart rate (N=41; F(1, 39) = 7.355, p = .015) correlated with greater divergence in false alarm rates between negative and neutral images. C) No such correlation was evident with cortisol levels (N=46; F(1, 44) = 0.794, p = .378). Shaded areas correspond to the standard error of fitted values.