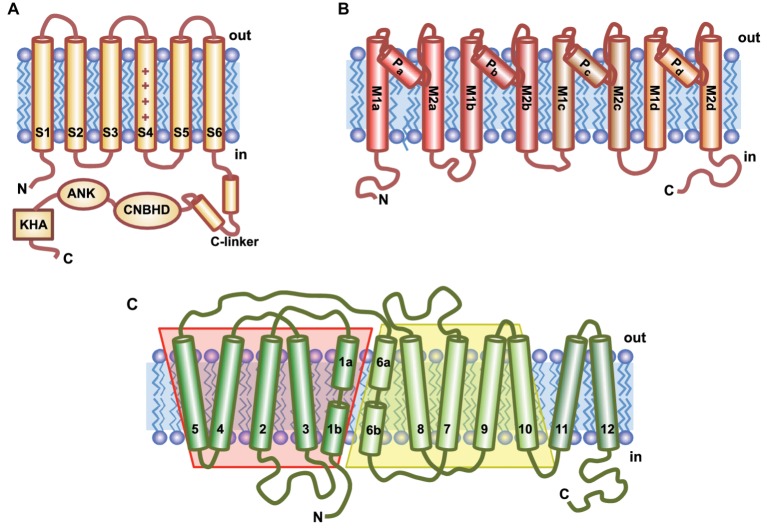
Figure 2.
Topological models of the main ion transporters involved in K+ nutrition. (A) Voltage-gated K+ channels contain six transmembrane domains (S1–S6); S4 is the voltage-sensor characterized by the array of positively charged amino acids (+). The long C-terminal tail contains several conserved domains: C-linker, a cyclic nucleotide binding homologous domain (CNBHD), an ankyrin domain (ANK), and a final region rich in hydrophobic and acidic residues (KHA). (B) HKT transporters have a channel-like structure that contains four identical subunits (a–d), each comprising two transmembrane helices (M1 and M2) connected by the P-loop involved in ion selectivity. (C) KT/HAK/KUP transporters have 12 putative transmembrane domains (TMs). TM1-5 and TM6-10 are predicted to fold in the same conformation but showing inverse symmetry.