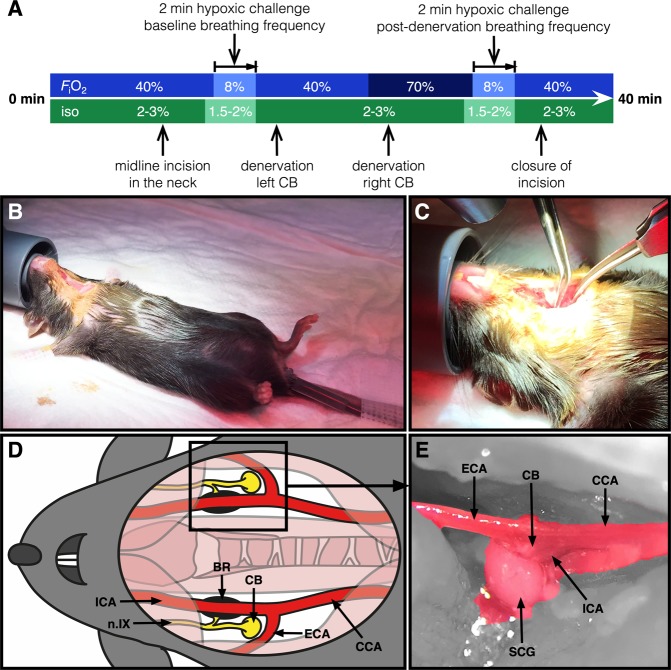
Figure 2.
Mouse model of bilateral carotid body denervation. Each depicted procedure is explained in the Materials and Methods section. (A) FiO2 and isoflurane (iso) levels and timing during the surgical procedure and HVR testing. In short, (B) anesthesia is induced and maintained by subcutaneous buprenorphine injection and isoflurane inhalation. A rectal temperature probe is applied, the animal is fixated, and a midline incision in the neck is made. (C) The bifurcation of the carotid artery accessed on each side by blunt preparation. A schematic (D) and microscopic anterolateral perioperative image (E) of the anatomy of the carotid chemoreceptor area is depicted (15× magnification) showing the carotid body (CB) (after removal of) the superior cervical ganglion (SCG), carotid baroreceptor (BR), glossopharyngeal nerve (n.IX), common carotid artery (CCA), external carotid artery (ECA), and the internal carotid artery (ICA).