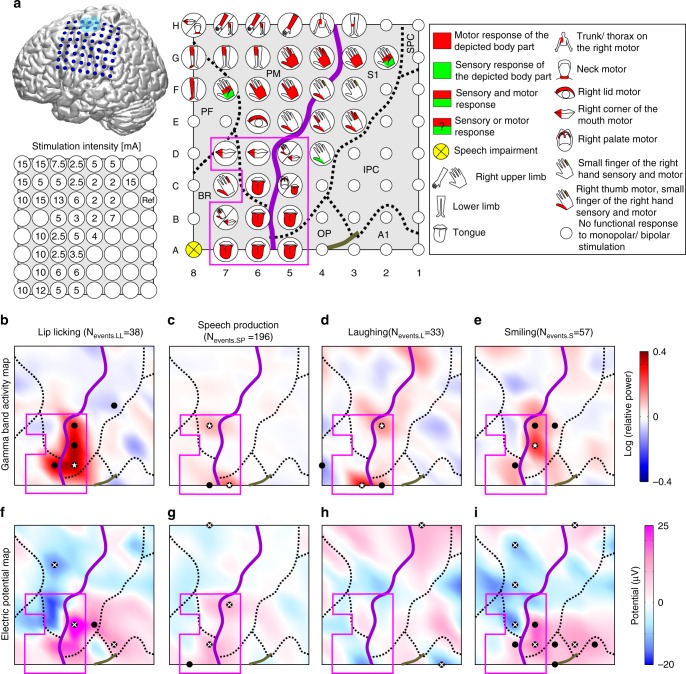
Fig. 2.
Electrocortical stimulation map and orofacial event-related brain activity maps of P1. a Position of the 8 × 8 electrode array visualized on a standard brain surface. Blue: seizure onset zone/area of multiple subpial transections. Electrocortical stimulation mapping (ESM): stylized body parts indicate ESM responses; motor and sensory responses shown in red and green, respectively. Magenta outline: borders of the ESM-defined mouth motor cortex. Purple and grey lines: central and lateral sulcus derived from individual post-implantation MRI, respectively. Black dotted lines: borders between cortical areas, determined by using the probabilistic anatomical maps from the Anatomy Toolbox 1.6 in SPM8. PF prefrontal cortex, BR Broca’s area, PM premotor cortex, S1 primary somatosensory cortex, IPC inferior parietal cortex, SPC superior parietal cortex. Stimulation intensity for all electrode contacts with ESM responses is shown beneath the standard brain. b–e Gamma band (55–200 Hz) activity maps related to the different orofacial movement classes; interpolated maps are shown (from left to right): lip licking (b), speech production (c), laughing (d) and smiling (e). Black dots indicate significant brain activity (sign test; p < 0.05 for <100 events and p < 0.0001 for >100 events; corrected for multiple comparisons), white stars indicate local maxima. f–i Electrical potential map related to the different orofacial movement classes; conventions as in b–e, but for the movement-related potentials (MRP)