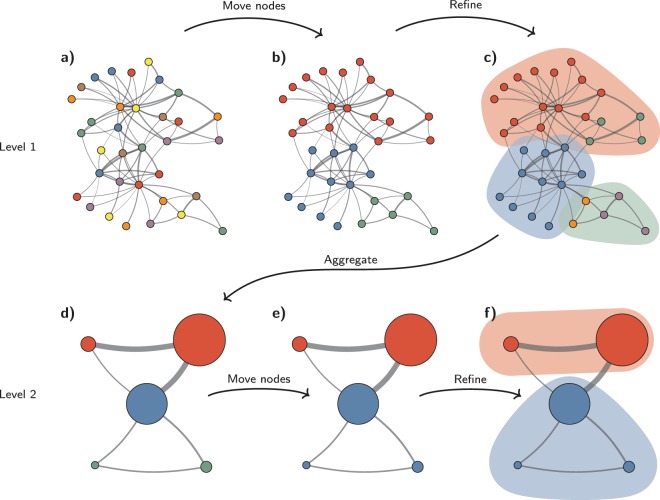
Figure 3.
Leiden algorithm. The Leiden algorithm starts from a singleton partition (a). The algorithm moves individual nodes from one community to another to find a partition (b), which is then refined (c). An aggregate network (d) is created based on the refined partition, using the non-refined partition to create an initial partition for the aggregate network. For example, the red community in (b) is refined into two subcommunities in (c), which after aggregation become two separate nodes in (d), both belonging to the same community. The algorithm then moves individual nodes in the aggregate network (e). In this case, refinement does not change the partition (f). These steps are repeated until no further improvements can be made.