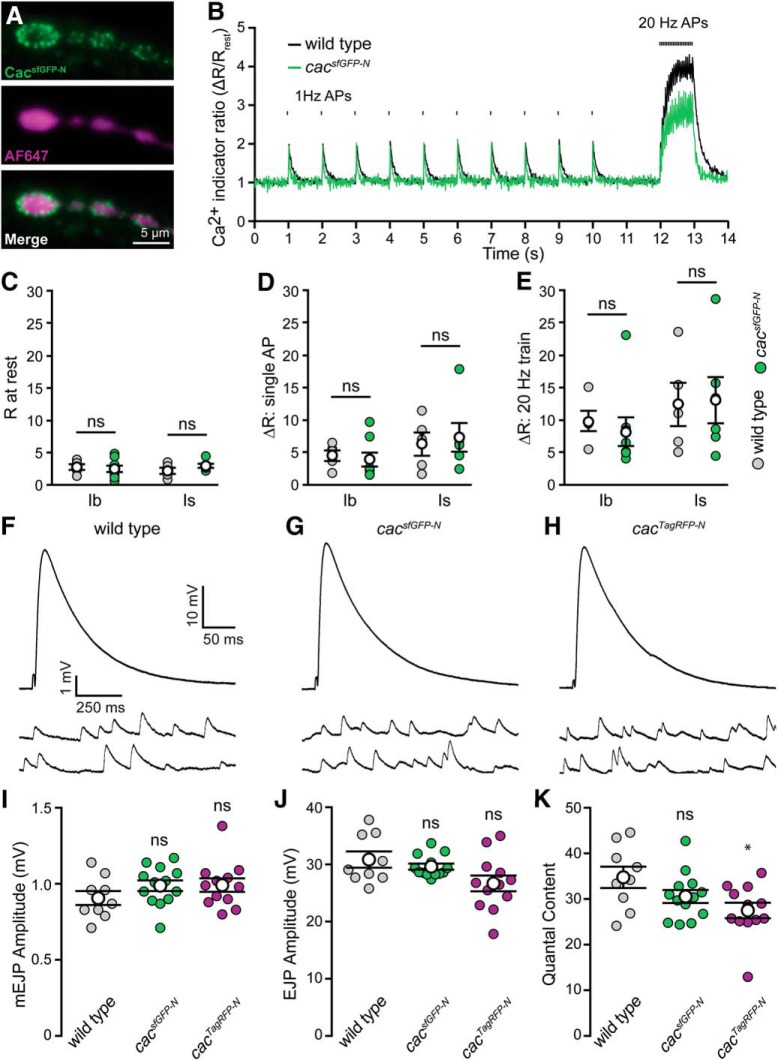
Figure 2.
Endogenous tagging of Cacophony does not perturb presynaptic Ca2+ influx or synaptic function. A, Live fluorescence images of type-Ib boutons from a cacsfGFP-N motor terminal showing CacsfGFP-N (top) and AF647-dextran (center), which was co-loaded with rhod-dextran (image not shown). B, Ratiometric fluorescence changes (rhod-dextran relative to AF647-dextran) in presynaptic motorneuron terminals during stimulation in wild type and cacsfGFP-N. An action potential was initiated every second, for a period of 10 s, followed by a 1 s, 20 Hz train of action potentials. C, Plot of average Ca2+ levels (R) in terminals before nerve stimulation for type-Ib and -Is terminals in wild-type and cacsfGFP-N boutons [wild-type Ib, 2.74 ± 0.44, one NMJ from each of 5 animals (N = 5); cacsfGFP-N Ib, 2.47 ± 0.49, N = 8, p = 0.69; wild-type Is, 2.16 ± 0.47, N = 5; cacsfGFP-N Is, 2.94 ± 0.32, N = 6, p = 0.21; Student's t test). D, Plot of the average amplitude of single action potential-mediated Ca2+ transients [ΔR; wild-type Ib, 4.50 ± 0.81, one NMJ from each of 5 animals (N = 5); cacsfGFP-N Ib, 3.90 ± 1.07, N = 8, p = 0.67; wild-type Is, 6.28 ± 1.79, N = 5; cacsfGFP-N Is, 7.33 ± 2.20, N = 6, p = 0.72; Student's t test]. E, Plot of the average amplitude of 1 s, 20 Hz action potential train-mediated Ca2+ transients [wild-type Ib, 9.71 ± 1.53, one NMJ from each of 5 animals (N = 5); cacsfGFP-N Ib, 8.13 ± 2.21, N = 8, p = 0.57; wild-type Is, 12.26 ± 3.36, N = 5; cacsfGFP-N Is, 12.94 ± 3.45, N = 6, p = 0.89; Student's t test]. F–H, Representative traces of EJPs and mEJPs recorded in 0.4 mm Ca2+ at wild-type (F), cacsfGFP-N (G), and cacTagRFP-N NMJs (H). I, mEJP amplitude is unaffected in cacsfGFP-N and cacTagRFP-N (wild type, 0.91 ± 0.05, n = 9 NMJs from 4 larvae; cacsfGFP-N, 0.99 ± 0.04, n = 13 NMJs from 4 larvae, p = 0.17, Student's t test; cacTagRFP-N, 0.99 ± 0.04, n = 12 NMJs from 4 larvae, p = 0.20, Mann–Whitney U test). J, EJP amplitude is unchanged between wild-type, cacsfGFP-N and cacTagRFP-N NMJs (wild type, 30.87 ± 1.41, n = 9 NMJs from 4 larvae; cacsfGFP-N, 29.64 ± 0.52, n = 13 NMJs from 4 larvae, p = 0.84, Mann–Whitney U test; cacTagRFP-N, 26.70 ± 1.39, n = 12 NMJs from 4 larvae, p = 0.05, Student's t test). K, Quantal content is similar between wild-type, cacsfGFP-N and cacTagRFP-N NMJs (wild type, 34.8 ± 2.3, n = 9 NMJs from 4 larvae; cacsfGFP-N, 30.6 ± 1.4, n = 13 NMJs from 4 larvae, p = 0.12, Student's t test; cacTagRFP-N, 27.5 ± 1.7, n = 12 NMJs from 4 larvae, p = 0.03, Mann–Whitney U test). Not significant (ns) and *p < 0.05.