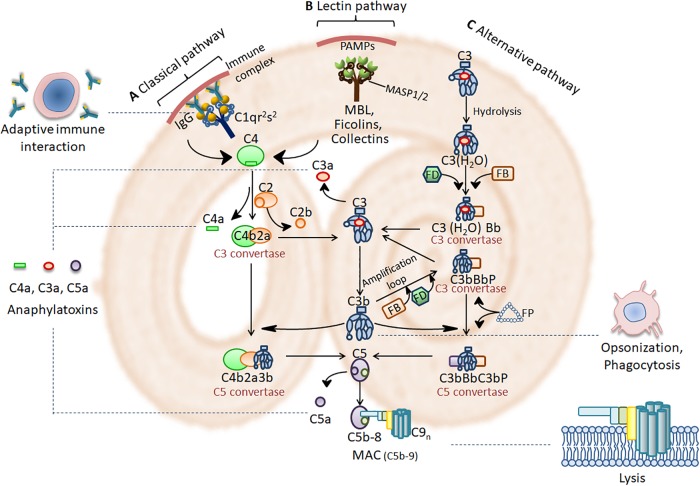
FIGURE 1.
Complement activation cascades and functions. (A) Immune complex (IC) activates the classical pathway through activating C1 complex (C1qr2s2). (B) PRMs such as MBL, ficolins and collectins, found in complexes with serine proteases (MASPs), bind to pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on the pathogen surface to activate the lectin pathway. Activation of the classical and lectin pathway leads to cleavage of C4 and C2 to form a C3 convertase (C4b2a). (C) The alternative pathway is initiated spontaneously by hydrolyzing C3 into C3(H2O) with factors FB, FD and FP. This leads to the formation of C3 convertases of the alternative pathway [C3(H2O)Bb or C3bBb]. Complement activation then comes to a core stage that C3 convertase cleave C3 into the anaphylatoxin C3a and the opsonin C3b. C3b then participates in the formation of the classical and lectin pathway C5 convertase (C4b2a3b) and the alternative pathway C5 convertase (C3bBbC3b). C5 convertase cleave C5 into the anaphylatoxin C5a and C5b. Afterwards, C5b assembles with C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 molecules on the target surface to form MAC (C5b-9). MAC is a 10-nm aperture inserting into the target membrane, which results in the lysis of invading pathogens. The anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a bind to their corresponding receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to mediate inflammation. C3b triggers opsonization which facilitate phagocytic removal of the target. Complement modulates a variety of immune activities and acts as a linker between the native and the adaptive immune response such as augmentation of antibody response and enhancement of immunologic memory.