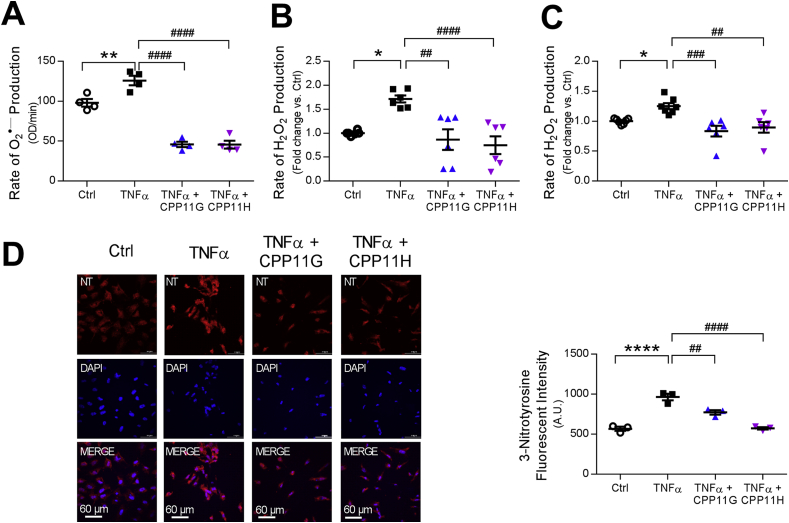
Fig. 2.
Nox2 inhibitors attenuate TNFα-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs). (A) Effects of CPP11G (10 μmol/l) and CPP11H (10 μmol/l) on TNFα (10 ng/ml)-stimulated extracellular superoxide () measured by hydropropidine (HPr+) Assay, n = 4. (**p < 0.01 vs. Ctrl, ####p < 0.0001 vs. TNFα). (B) Effects of CPP11G (10 μmol/l) and CPP11H (10 μmol/l) on TNFα (10 ng/ml)-stimulated hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production measured by coumarin-7-boronic acid (CBA) Assay, n = 6. (*p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, ##p < 0.01 vs. TNFα, ####p < 0.0001 vs. TNFα). (C) Effects of CPP11G (10 μmol/l) and CPP11H (10 μmol/l) on TNFα (10 ng/ml, 10 min)-stimulated H2O2 production examined by Amplex Red Assay, n = 6–7. (*p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl, ##p < 0.01 vs. TNFα, ###p < 0.001 vs. TNFα). (D) Immunofluorescence microscopy (20× magnification) detection of 3-nitrotyrosine (red) formation upon 24h TNFα (10 ng/ml) stimulation in the presence or absence of CPP11G or CPP11H (10 μmol/l). Nuclei were labelled with DAPI (blue). Fluorescence intensity was quantified from 3 images/group, n = 3 independent experiments. (****p < 0.0001 vs. Ctrl, ##p < 0.01 vs. TNFα, ####p < 0.0001 vs. TNFα).