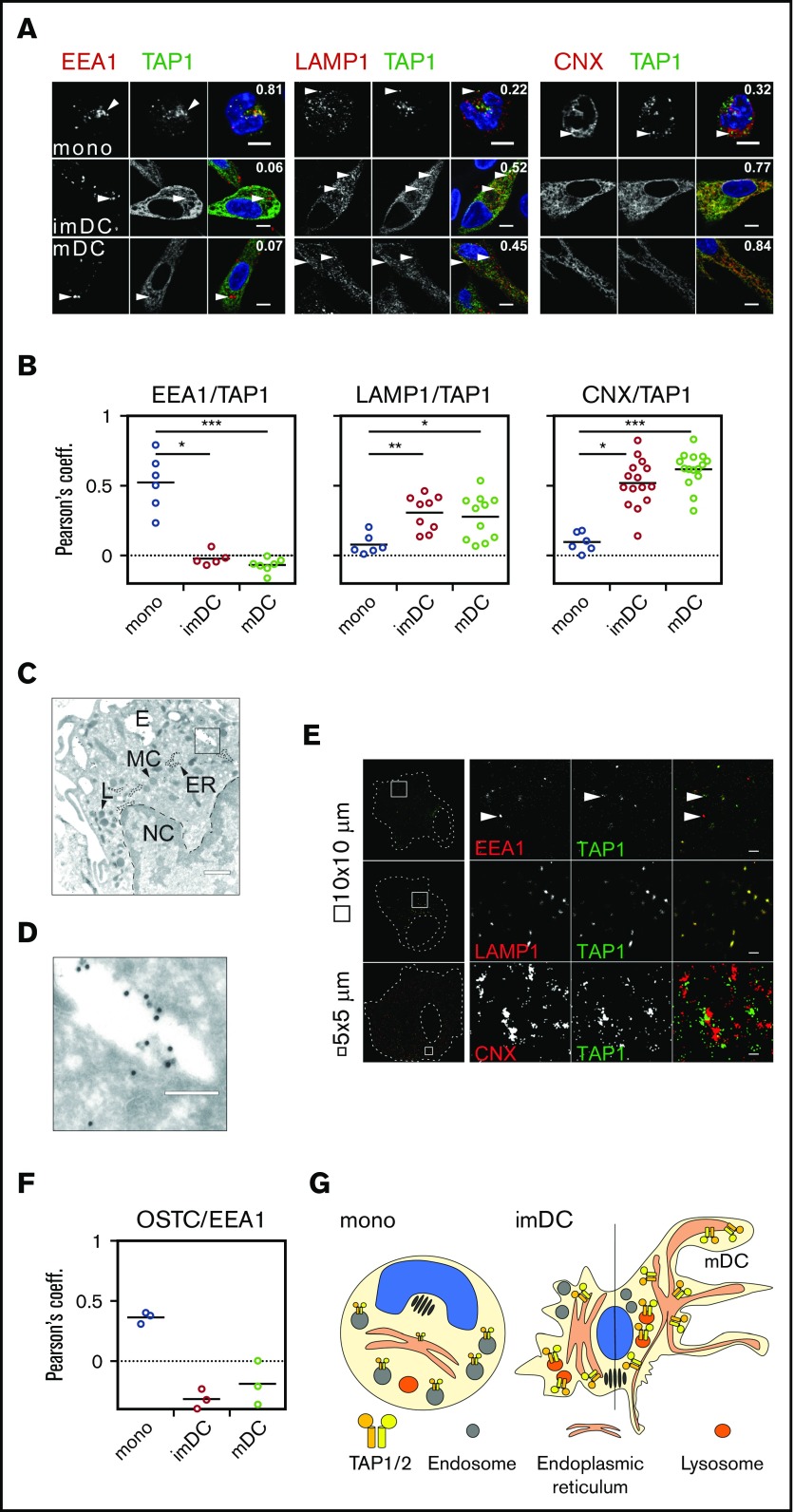
Figure 4.
TAP location changes from endosomes to the ER and lysosomes. (A) Immunofluorescent staining of the early endosomes (EEA1), lysosomes (LAMP1), the ER membrane marker calnexin (CNX), and TAP1 in monocytes, imDCs, and mDCs. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Statistical analysis of Pearson coefficients obtained in 4 independent experiments (white circles represent donors; the mean is shown as a black line). ***P ≤ .0001; **P ≤ .001; *P ≤ .05; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s correction for multiple comparison. (C) Electron microscopy of monocytes. Scale bar, 500 nm. (D) Magnification of the area indicated in panel C. Scale bar, 150 nm. (E) Stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (N-STORM) of mDCs stained for EEA1, LAMP1, CNX, and TAP1. Scale bars, 1 µm; CNX/TAP1 photo scale bar, 0.5 µm. One of 2 independent experiments is shown. (F) Statistical analysis of Pearson coefficients obtained in 2 independent experiments of OST and TAP1 costaining (white circles represent donors; the mean is shown as a black line). (G) Model of TAP relocalization during moDC differentiation. TAP is expressed in EEA1+ endosomes of monocytes and relocalizes to the ER (CNX+) and LAMP1+ lysosomes in moDCs. The size of TAP1/2 heterodimer in the cartoon is according to its protein expression level and inversely correlates with its activity. The nucleus is shown in blue and the Golgi apparatus as brown tubular structures. E, endosome, TAP1 (15-nm gold particles); ER, ER membrane stacks; L, lysosome; MC, mitochondria; NC, nucleus.