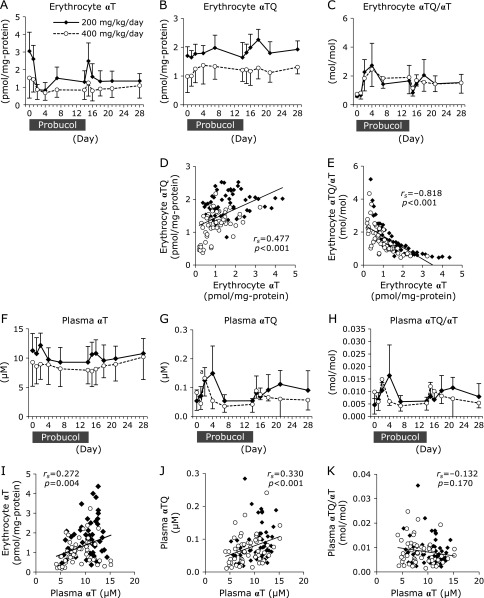
Fig. 2.
The changes in α-tocopherol (αT) and α-tocopherylquinone (αTQ) concentrations in erythrocytes and plasma. The concentrations of αT (A) and αTQ (B) in erythrocytes were measured using HPLC-ECD. The ratio of αTQ to αT (αTQ/αT) in erythrocytes was calculated (C). (D) The correlation between αT and αTQ concentrations in erythrocytes. (E) The correlation between αT level and the ratio of αTQ/αT in erythrocytes. The concentrations of αT (F) and αTQ (G) and αTQ/αT ratio (H) in plasma were analyzed. (I) The correlation between the αT concentration in plasma and that in erythrocytes. (J) The correlation between plasma αT- and αTQ-concentration. (K) The correlation between αT level and the ratio of αTQ/αT in plasma. The data are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was carried out using ANOVA. ap<0.05 compared to the initial (day 0) value of the same individual. To analyze the correlations, the normality of data distribution was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test, and the correlations were assessed by Spearman’s exact test. Solid diamonds indicate probucol 200 mg/kg/day macaque group. Open circles indicate probucol 400 mg/kg/day administered macaque group.