Figure 1.
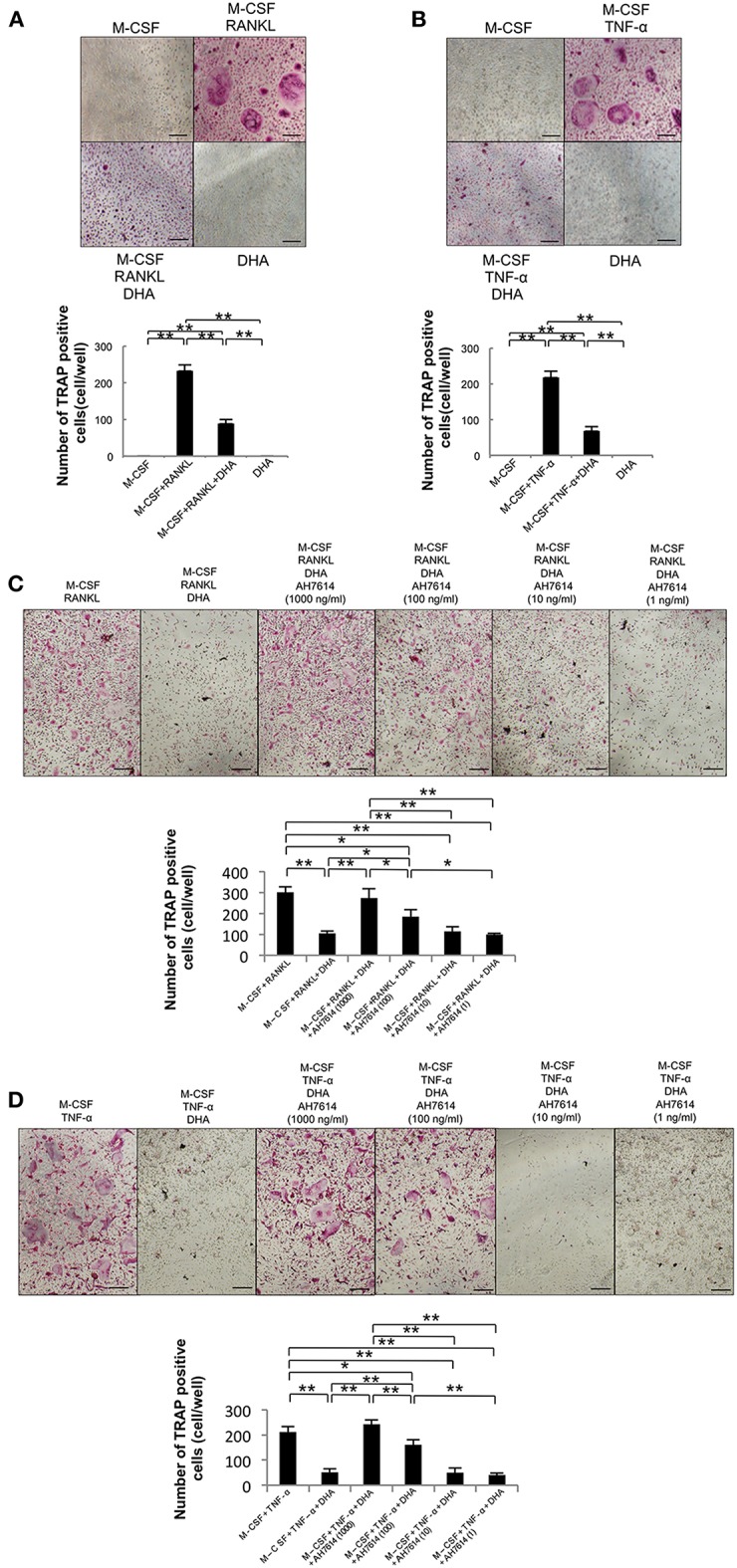
DHA inhibits RANKL- and TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation via GPR120 in vitro. (A) Microscopic images and numbers of TRAP-positive cells following RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. Osteoclast precursors were cultured with M-CSF, M-CSF+RANKL, M-CSF+RANKL+DHA, or M-CSF+DHA for 5 days, followed by staining with TRAP solution. (B) Microscopic images and numbers of TRAP-positive cells following TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation. Osteoclast precursors were treated with M-CSF, M-CSF+TNF-α, M-CSF+TNF-α+DHA, or M-CSF+DHA for 5 days, followed by staining with TRAP solution. (C) Microscopic images and numbers of TRAP-positive cells following RANKL-induced osteoclast formation under AH7614 treatment. Osteoclast precursors were cultured with M-CSF+RANKL, M-CSF+RANKL+DHA, or M-CSF+RANKL+DHA and various concentration of AH7614 (1,000, 100, 10, and 1 ng/mL). (D) Microscopic photos and numbers of TRAP-positive cells following TNF-α-induced osteoclast formation under AH7614 treatment. Osteoclast precursors were cultured with M-CSF+TNF-α, M-CSF+TNF-α+DHA, or M-CSF+TNF-α+DHA and various concentration of AH7614 (1,000, 100, 10, and 1 ng/mL). Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 4; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05). Statistical significance was determined by Scheffe's test. Scale bars = 100 μm.
