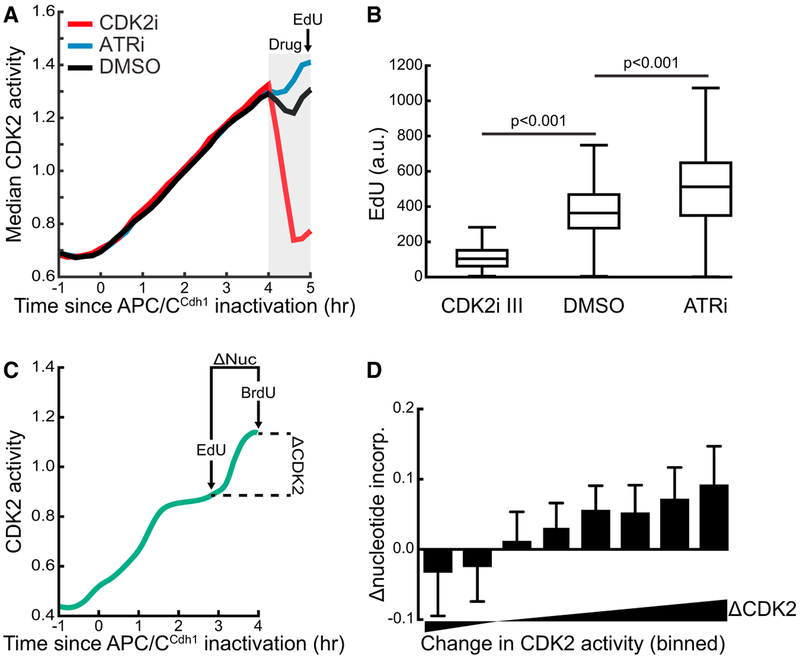
Figure 4. Endogenous Fluctuations in CDK2 Activity Dynamically Decrease and Increase Global DNA Synthesis Rate.
(A) Median traces of cycling cells gated for cells in S phase when treated with indicated drugs (n > 500 for each condition). One of n = 2 biological replicates.
(B) Boxplot of EdU values in individual cells from (A) treated with the indicated drugs.
(C) Experimental design for co-labeling of cells with EdU and BrdU to compare DNA synthesis rate at different points in time in individual cells. Changes in CDK2 activity and changes in nucleotide incorporation rate were analyzed in individual S-phase cells.
(D) Cycling cells in S phase at the time of nucleotide addition were binned based on the change in CDK2 activity from EdU pulse to BrdU pulse and median Dnucleotide values ± SEM were calculated for each bin (n > 70 cells for each bin). Bins range from −0.10 to 0.25 with a step size of 0.05. By linear regression, r2 = 0.96. One of n = 2 biological replicates. incorp., incorporation.