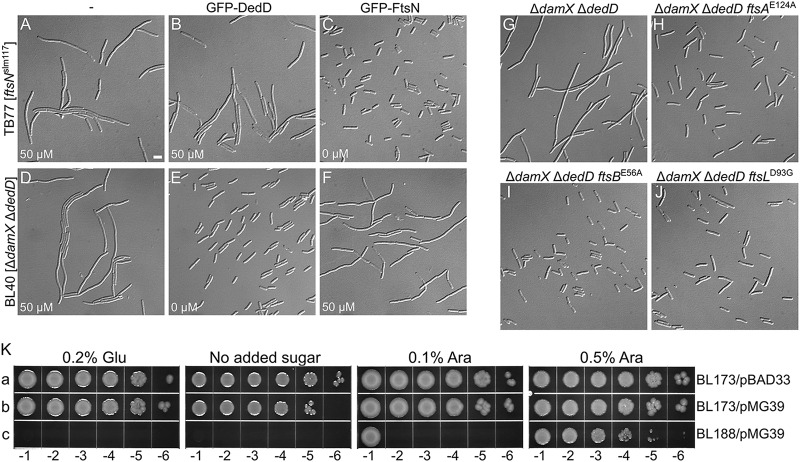
FIG 6.
DedD functions independently of FtsN. (A to J) Cells were grown for ∼5 mass doublings to an OD600 of 0.5 to 0.6 in LB with 50 μM IPTG (A, B, D, and F) or without inducer (C, E, and G to J) and were imaged live (A to F) or after chemical fixation (G to J). Bar, 4 μm. (A to F) Little to no cross-functionality of FtsN and DedD. Cells of strain TB77 [ftsNslm117] (A to C) and BL40 [ΔdamX ΔdedD] (D to F) carrying pMLB1113ΔH [Plac::] (A and D), pFB236 [Plac::gfp-dedD] (B and E), or pCH201 [Plac::gfp-ftsN] (C and F) are shown. (G to J) EFtsN*-suppressing mutations in ftsA, ftsB, or ftsL also suppress the division defect associated with the absence of DedD. Shown are cells of strains BL40 [ΔdamX ΔdedD] (G), CH178 [ΔdamX ΔdedD ftsAE124A] (H), CH177 [ΔdamX ΔdedD ftsBE56A] (I), and CH181 [ΔdamX ΔdedD ftsLD93G] (J). (K) Depletion of DedD from ftsBE56A ΔftsN cells is lethal. Strains BL173 [ftsBE56A ΔftsN] (a and b) and BL188 [ftsBE56A ΔftsN ΔdedD] (c), carrying pMG36 [PBAD::dedD] (b and c) or the vector control pBAD33 [PBAD::] (a), were grown overnight in LB with 0.5% arabinose. The cultures were serially diluted in LB to an OD600 of 1.0 × 10x, and 5 μl of each dilution was spotted on LB agar containing glucose, arabinose, or neither, as indicated. The plates were incubated for 20 h.