Figure 4.
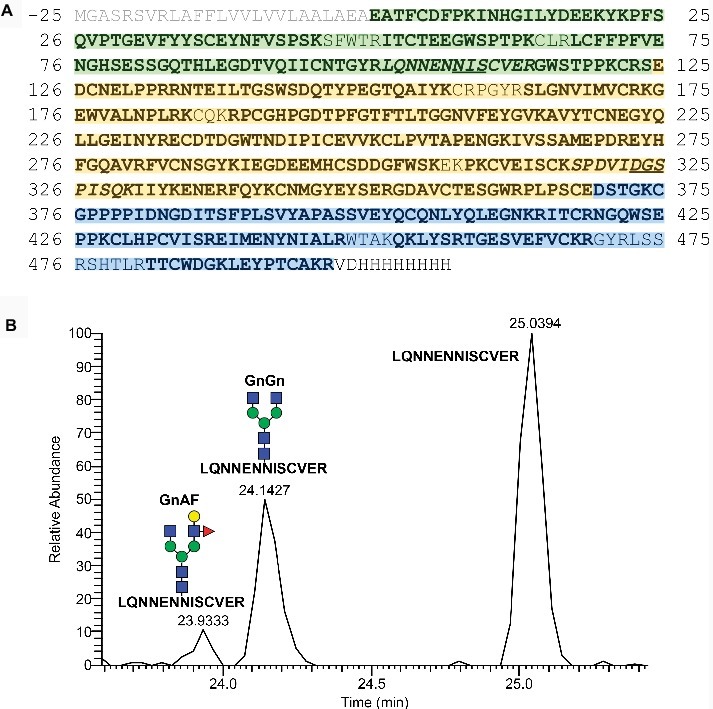
Sequence and domain structure of MFHR1 and mass spectrometric sequence and N-glycosylation analyses. (A) Mature MFHR1 sequence (black) fused to the AP1-signal peptide (grey). The amino acid positions relating to the mature protein are given. Negative numbers refer to the signal peptide. The amino-terminal portion of MFHR1 is composed of the first two SCRs of FHR1 (green), followed by the catalytically active SCRs 1-4 from FH (yellow). The C-terminus includes the surface-binding SCRs 19-20 from FH (blue) followed by a His-tag. Peptides identified by mass spectrometry are shown in bold and the putative N-glycosylation site NIS (Asn108) and the deamidated site DGS (Asn323 ➔ Asp323), are underlined, corresponding mass spectrometric detected tryptic peptides are shown in italics. (B) Elution profiles (extracted ion chromatogram, EIC) of the tryptic peptide (102LQNNENNISCVER113) which flanks the glycosylation site NIS (Asn108) with and without N-glycosylation. Peak identity was confirmed by m/z-value and charge state on MS1- and by reporter ions on MS2-level (see Supplementary Figure 4 for further information). Peak quantification revealed an N-glycan occupancy at Asn108 of 35%, which in total consisted of 86% GnGn−, nearly 14% GnAF structures and < 1% of N-glycans with terminal mannoses, all of them lacking plant specific core xylose and fucose. For the deamidated site (Asn323 ➔ Asp323) no N-glycosylation was detectable. Gn: N-acetylglucosamine, A: galactose, F: Fucose – referring to the terminal sugar residues.
