Figure 1.
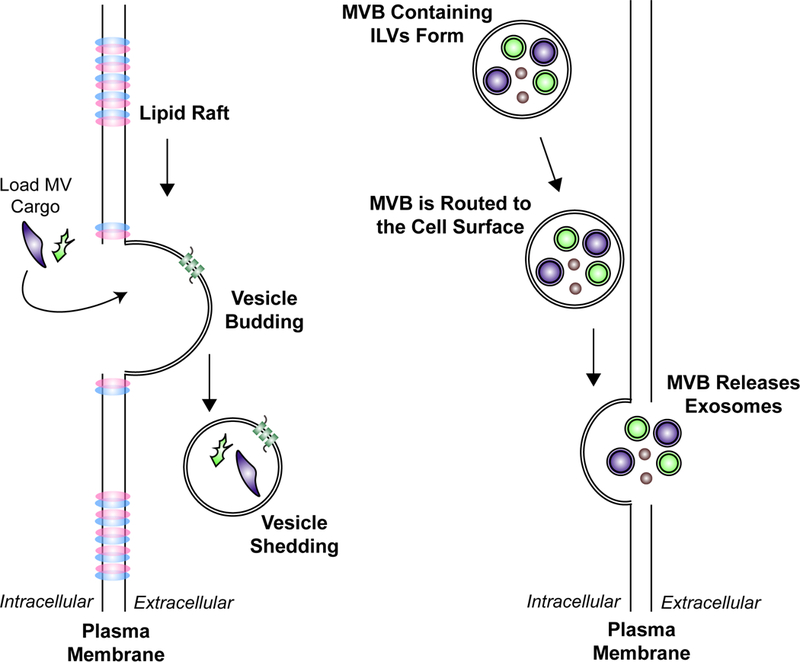
The mechanisms that give rise to the two major classes of EVs, MVs and exosomes. A) MV formation is initiated by the outward budding of the plasma membrane at lipid-raft-like domains. The MV is then loaded with various cargo, before it is shed into the extracellular space. The size of MVs range from 200–2000 nm. B) Exosomes represent the second major class of EVs. They are derived as MVBs containing ILVs are routed to the cell surface. The MVB then fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents. The ILVs that are released are referred to as exosomes. This class of EVs is typically 50–120 nm in diameter.
