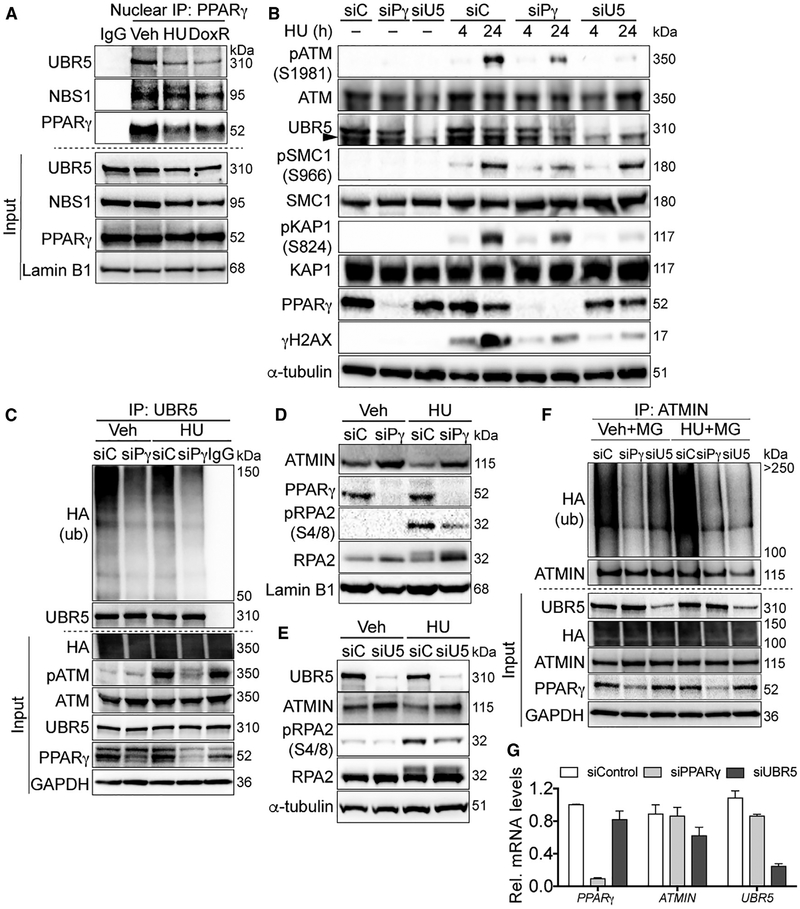
Figure 2. PPARγ Promotes ATM Signaling by Increasing UBR5-Mediated ATMIN Ubiquitination in 293T Cells.
(A) Representative immunoblots of endogenous nuclear PPARγ interactions with MRN and UBR5 at baseline and upon DNA damage induced by HU and doxorubicin (DoxR).
(B) Representative immunoblots of HU-induced pATM and its targets with PPARγ or UBR5 depletion.
(C) Representative immunoblots of reduced UBR5 binding to ubiquitinated proteins with PPARγ depletion.
(D and E) Representative immunoblots of ATMIN and pRPA2 levels with PPARγ (D) or UBR5 (E) depletion upon HU treatments.
(F) Cells were transfected with HA-tagged ubiquitin and subsequently the siRNA as indicated. Cells were treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (MG) for 2 h before lysis in a denaturing buffer. Endogenous ATMIN was immunoprecipitated to determine its polyubiquitinated form. Representative immunoblots show effects of PPARγ or UBR5 depletion on endogenous ATMIN ubiquitination detected by anti-hemagglutinin (HA) antibody.
(G) Quantitative real-time PCR shows effects of PPARγ or UBR5 depletion by the respective siRNA on ATMIN mRNA levels (normalized to β-actin mRNA).
siC, siControl; siPg, siPPARγ; siU5, siUBR5; Veh; vehicle. Error bars, mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S3.