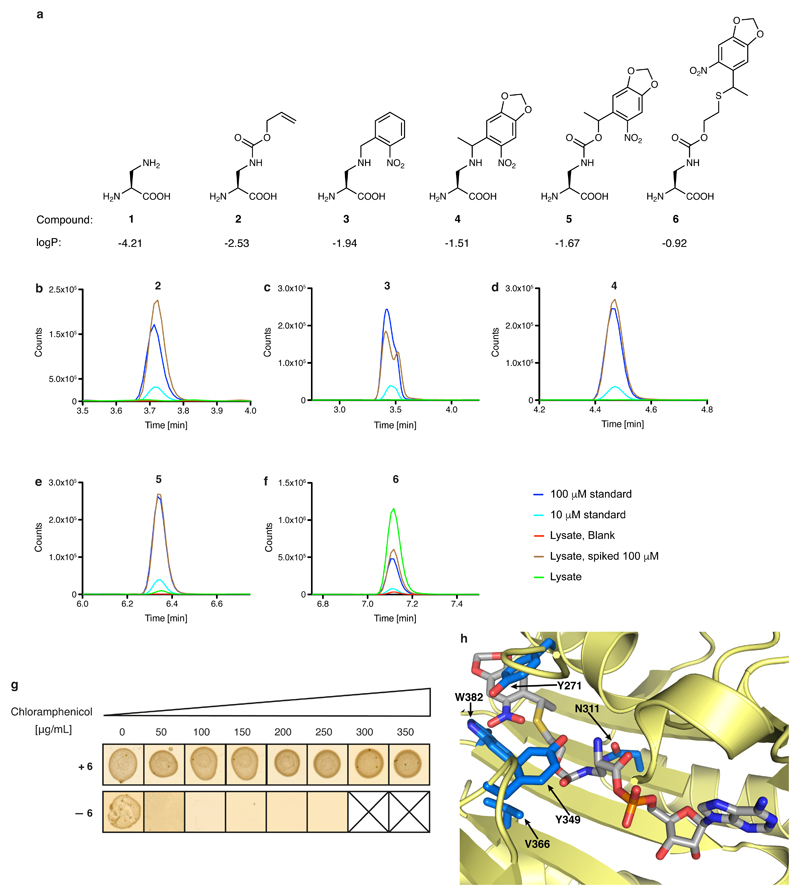
Extended Data Fig. 2. Genetically directing DAP incorporation in recombinant proteins.
a, Structure of DAP and the protected versions investigated herein. 1, 2,3-diaminopropionic acid (DAP); 2, (S)-3-(((allyloxy)carbonyl)amino)-2-aminopropanoic acid; 3, (S)-2-amino-3-((2-nitrobenzyl)amino)propanoic acid; 4, (2S)-2-amino-3-((1-(6-nitrobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)ethyl)amino)propanoic acid; 5, (2S)-2-amino-3-(((1-(6-nitrobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)ethoxy)carbonyl)amino)propanoic acid; 6, (2S)-2-amino-3-(((2-((1-(6-nitrobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)ethyl)thio)ethoxy)carbonyl)amino)propanoic acid. Calculated logP values are indicated (calculated using the Molinspiration molecular property calculation services at www.molinspiration.com/cgi-bin/properties). b–f, Determining the intracellular concentration of compounds 2–6 by an LC–MS assay, performed on extracts. The dark-blue trace represents a 100 µM standard for each compound. The light-blue trace represents a 10 µM standard for each compound. The red trace results from cells grown in the absence of the compound. The brown trace results from cells grown in the absence of the compound, but spiked with the compound to 100 µM. The green trace results from cells grown in the presence of 1 mM compound. The experiments were repeated in two biological replicates with similar results. g, Phenotyping of the DAPRS/tRNACUA pair. Cells containing the DAPRS/tRNACUA pair and cat(112TAG) (encoding a chloramphenicol-resistance gene containing an amber stop codon (TAG) at codon 112) were plated in the presence or absence of 6 on the indicated concentrations of chloramphenicol. The experiment was performed in two biological replicates with similar results. h, The side chain of 6 (grey sticks) was modelled into the active site of PylRS using a co-crystal structure of PylRS and adenylated pyrrolysine (PDB accession number 2ZIM31). PylRS is displayed in pale yellow and amino-acid positions randomized in DAPRSlib are shown in marine blue.