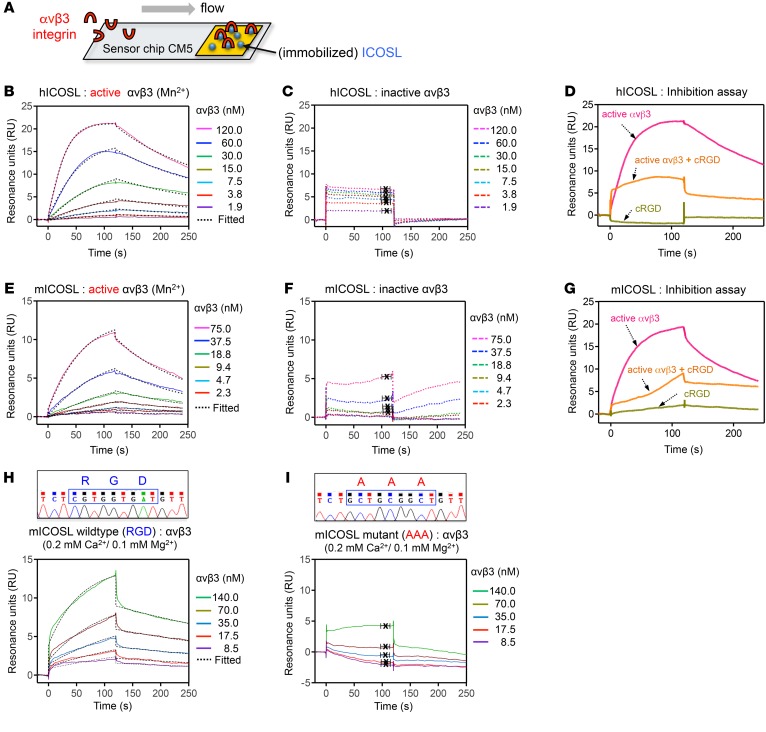
Figure 2. ICOSL binds to active αvβ3 integrin through its RGD motif.
(A) Schematic of a gold surface with ICOSL protein on a sensor chip CM5 and associated protein (αvβ3 integrin) over which buffer is flown in SPR assay. (B–I) SPR sensorgrams depicting interaction of immobilized human ICOSL (hICOSL, B–D) or mouse ICOSL (mICOSL, E–I) with αvβ3 integrin. These bindings were tested in the presence (B and E, active form of αvβ3) or absence (C and F, inactive form of one with EDTA in the binding buffer) of Mn2+. (D and G) SPR used in an inhibition experiment with cRGDfv. Injection of αvβ3 integrin only (D, 120 nM αvβ3 or G, 150 nM αvβ3) resulted in a binding signal for immobilized hICOSL or mICOSL alone (pink line). Preincubation with cRGDfv (3 μM or 15 μM) significantly reduced the binding for ICOSL, indicating that the RGD peptide competes with ICOSL for binding to αvβ3 (orange line). cRGDfv alone was used as a control (green line). (H and I) SPR sensorgrams showing the binding between WT (H) or mutant (I) mICOSL protein and αvβ3 integrin in the presence of physiologically relevant divalent ions, Ca2+ (0.2 mM) and Mg2+ (0.1 mM). The average KD values were determined from at least 3 independent experiments. Rate constants (ka and kd) were determined by kinetic fitting (black dotted line) of the sensorgrams using 1-to-1 Langmuir binding equation, and KD values for B, E, and H were calculated by kd/ka (B, KD = 16.2 ± 4.0 nM for hICOSL/αvβ3 with Mn2+; E, KD = 24.2 ± 6.5 nM for mICOSL/αvβ3 with Mn2+; H, KD = 21.3 ± 1.2 nM for WT mICOSL/αvβ3 with Ca2+/Mg2+). KD values for C, F, and I were calculated from steady-state affinity fittings (C, KD = 411.8 ± 164.1 nM for hICOSL/αvβ3; F, KD ≥ 2 mM for mICOSL/αvβ3; I, KD = 0.83 ± 0.8 mM for mutant mICOSL/αvβ3 with Ca2+/Mg2+).