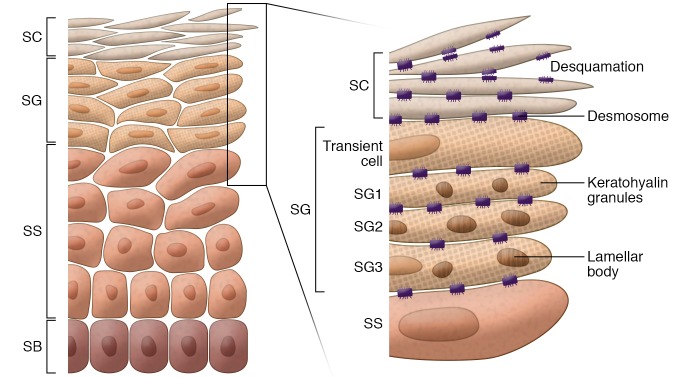
Figure 1. Structure of human epidermis.
Human epidermis is composed of SB, SS, SG, and SC. In SC, corneocytes (flattened and denucleated keratinocytes) and intercellular lipids released from lamellar bodies form the “brick and mortar” structures. The cornified envelope, a highly cross-linked layer of insoluble proteins, forms under the corneocyte cell membrane, anchored by extracellular lipids. Components of the cornified envelope (keratohyalin granules, a source of filaggrin) and lamellar bodies (containing lipids, lipid-processing enzymes, corneodesmosin, proteases, and protease inhibitors) are formed in SG. The surface of the SC is shed off by degradation of corneodesmosomes via the activity of several proteases.