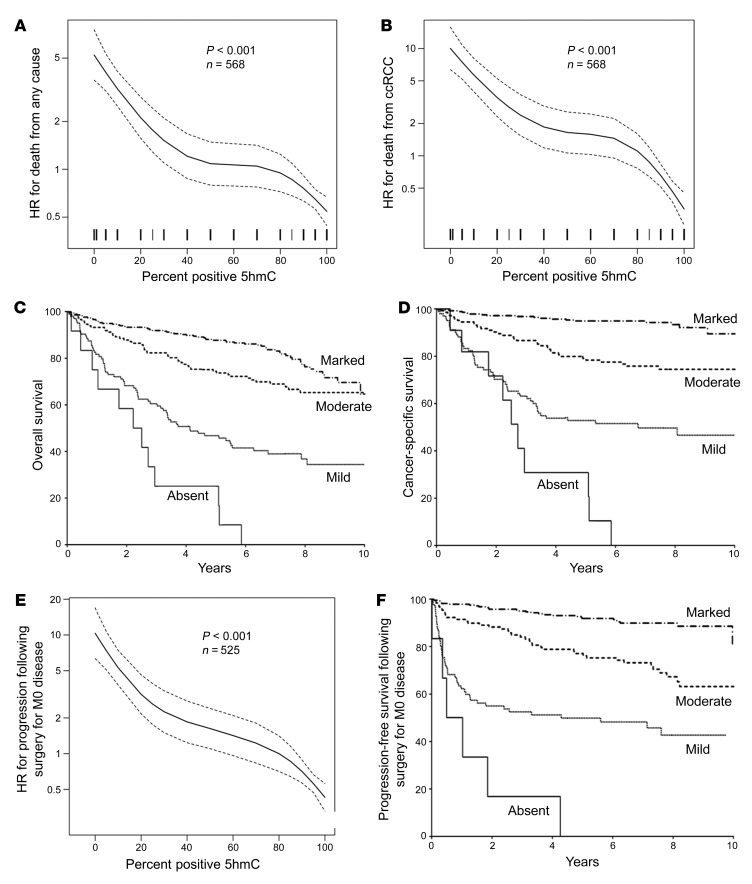
Figure 2. Loss of 5hmC is an independent prognostic factor in ccRCC and predicts shortened time to metastatic disease after surgical resection for M0 disease.
(A) Univariable association of percentage positive for 5hmC with death from any cause (HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.79–0.85; P < 0.001; n = 568 patients). Dotted lines represent 95% CI. (B) Univariable association of percentage positive for 5hmC with death from RCC (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.70–0.78; P < 0.001; n = 568 patients). Dotted lines represent 95% CI. (C) Univariable association of 5hmC intensity with OS. Median OS in the absent, mild, and moderate 5hmC intensity cohorts occurred at 2.4, 4.1, and 10.5 years, respectively. Median OS in the marked group has not been reached. (D) Univariable association of 5hmC intensity with CSS. Median CSS in the absent and mild intensity cohorts occurred at 2.7 and 6.8 years, respectively. Median CSS in the moderate and marked 5hmC intensity group has not been reached. Ten-year CSS in the marked 5hmC intensity group was 90%. (E) Univariable association of percentage positive for 5hmC with progression following surgery for M0 disease (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.72–0.80; P < 0.001). Dotted lines represent 95% CI. (F) Univariable association of 5hmC intensity with PFS among M0 patients. Median PFS in the absent and mild intensity cohort occurred at 0.8 and 4.3 years, respectively. Median CSS in the moderate and marked 5hmC intensity group has not been reached. Ten-year PFS in the marked 5hmC intensity group was 81%.