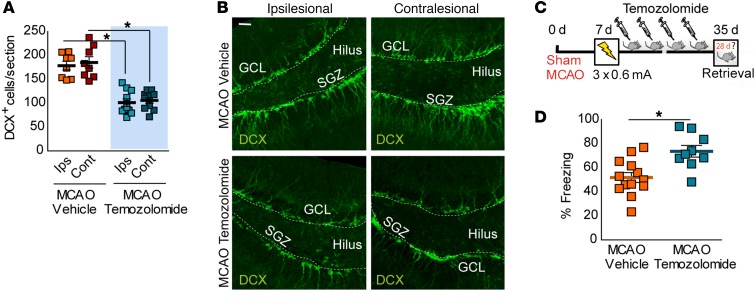
Figure 6. TMZ treatment after stroke mitigates hippocampus-dependent memory deficits.
(A and B) Number of DCX+ cells in MCAO mice treated with vehicle or TMZ. Representative images of DCX+ cells (B, green) in MCAO mice treated with vehicle or TMZ. Scale bar: 30 μm. For A, 2-way ANOVA analysis showed a significant effect of TMZ in the number of DCX+ cells (F(1,32) = 81.85; P < 0.0001) in both ipsi- and contralesional sides (Bonferroni’s post hoc: *P < 0.05 vs. MCAO vehicle; MCAO vehicle, n = 8; MCAO TMZ, n = 9) at 35 days. (C) Experimental design for poststroke neurogenesis inhibition by TMZ. Seven days after ischemia, mice were subjected to CFC (0.6 mA × 3), and 24 hours later, they were treated i.p. with TMZ (25 mg/kg) for 4 weeks (3 days per week) and tested in the CFC at the end of the treatment. (D) Percentage of freezing response in vehicle- or TMZ-treated ischemic mice 35 days after CFC (*P < 0.05 vs. MCAO vehicle; MCAO vehicle, n = 13; MCAO TMZ, n = 9). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Data were compared by using nonparametric 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U tests (D) or nonparametric 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc testing (A).