Figure 2. The dynamic and complex interaction between risk factors, disease phenotypes and endotypes, and expression modulators in allergic diseases in the context of precision medicine.
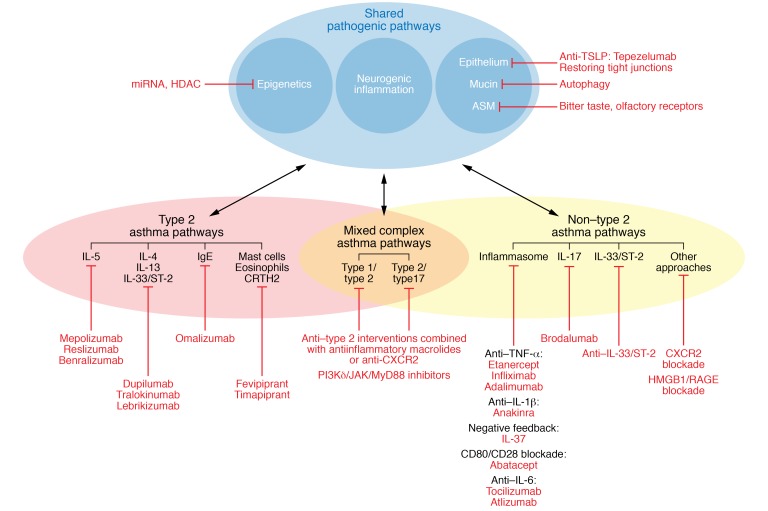
In type 2 asthma, four main pathways can be targeted: the IgE pathway (omalizumab), the IL-5 pathway (mepolizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab), the IL-4/IL-13 pathway (dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab), and the CRTH2 receptor (fevipiprant and timapiprant). In non–type 2 asthma, three main pathways can be targeted: the inflammasome pathway (anti–TNF-α interventions such as etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab; anti–IL-1β interventions such as anakinra; anti–IL-6 targeting with tocilizumab or atlizumab; negative feedback with IL-37; or CD80-CD28 blockade with abatacept), the IL-17 pathway (brodalumab), or the anti–IL-33 pathway, with CXCR2 and HMGB1/RAGE blockade as additional approaches. For the mixed complex endotypes, a combination of anti–type 2 interventions with antiinflammatory macrolides or anti-CXCR2 can be indicated. As an alternative, PI3Kδ/JAK/MyD88 inhibitors might block the upstream effects of type 1, type 2, and type 17 cytokines.